Rose of Leary model explained

Rose of Leary: this article explains the Rose of Leary by Timothy Leary in a practical way. Next to what it is (theory and basics), thsi article also highlights the Model and it’s dimensions, some practical examples, complementarity theory and a downloadable Rose of Leary test to get started. Enjoy reading!
What is the Rose of Leary? The theory
Do difficult people exist? This basic question immediately leads to another question. Why is certain behaviour perceived as difficult by other people? To get a better understanding of this perception, psychologist Timothy Leary distinguished four basic behaviours, which he subdivided into nuances. It’s called the Rose of Leary.
In the Rose of Leary it is not about the typing of human nature but rather about getting a clearer understanding of the impact of behaviour on others and the interaction between people. According to Timothy Leary, people do have a preference for a certain type of behaviour.
Rose of Leary Model is about basic behaviour
In order to clarify human behaviour and the interaction between people, Timothy Leary developed a communication model, named the Rose of Leary Model, based on a horizontal and a vertical axis.
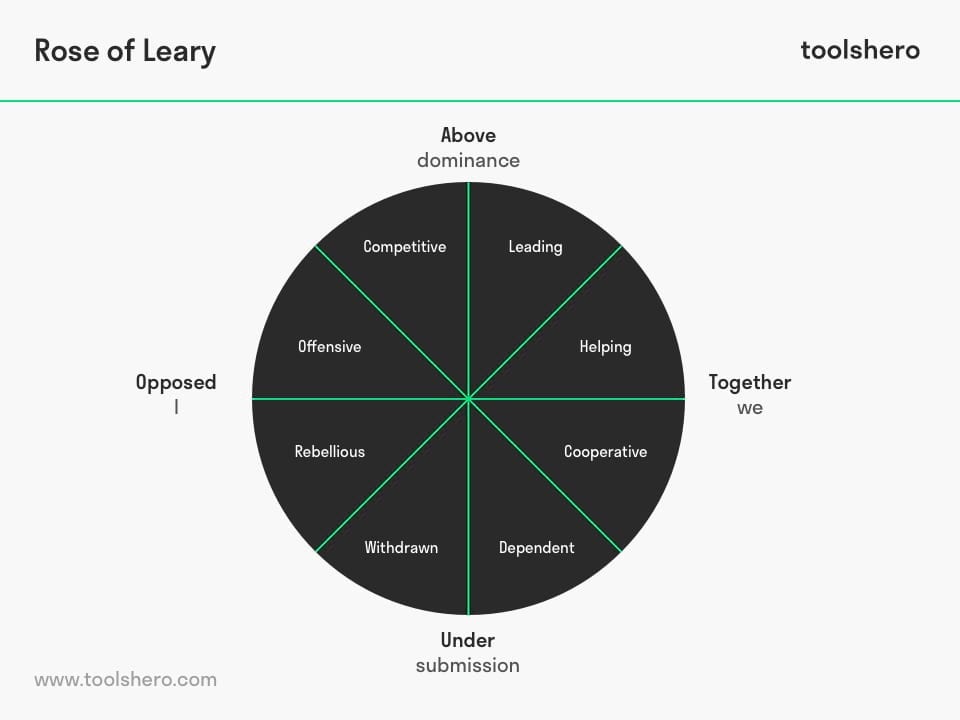
Figure 1 – the Rose of Leary Model
The horizontal axis focuses on relationships with others and the vertical axis focuses on attitude to others. The four directions form a rose from which the name of Timothy Leary ’s theory has been derived.
He referred to the north axis as the above behaviour, the south axis as the below behaviour, the west axis as the ‘opposed’ behaviour and the east as the together behaviour. Timothy Leary distinguishes additional nuances in these four basic behaviours such as above- together, above- opposed, below-together and below-opposed.
Above behaviour
Above behaviour is about active, initiating and leading behaviour. The degree of dominance is determined by the other party.
Below behaviour
Below behaviour is about submissive behaviour, the individual does not get involved, effaces himself or displays very modest behaviour.
Opposed behaviour
Opposed behaviour is about people who are aggressive and do not agree with other people unquestioningly. They want thorough explanations and motivations before they take action. This could develop into defiant behaviour.
Together behaviour
This is about an ideal situation in which people can work as a team and in which people are receptive to other people’s opinions.
Examples of Rose of Leary
According to Timothy Leary, it is about action-reaction. Below you will find some examples of everyday situations. Try to recognise the action-reaction patterns in the image above.
2 colleagues work together in the office
At some point, one of the colleagues pushes his office chair back abruptly and says to his colleague: ‘I have to stick something together and, once again, there’s no adhesive tape. Why did you not order it sooner?’ The other colleague is offended and responds: ‘I can’t think of everything, do it yourself!’
A project team member and the project manager meet at the coffee machine
The team member says to the project manager: ‘I don’t know what to do anymore, I’m never going to get the job done.’ To which the project manager then says: ‘come on now! You can do it, especially with the help of the right people. What needs to be done? What exactly is the problem?’
Two other colleagues bump into each other while out walking during the lunch break
One of them is sitting on a bench with a long face and says: ‘I don’t feel like doing anything on this rainy day. And on top of that, it’s Monday.’ The colleague continues to complain, to which the other says with an irritated tone: ‘If you don’t feel like doing anything, please complain about it to someone else. I’ve had enough of your remarks!’
Employee at a company receives an app
An HR employee at a company receives an app from her colleague:‘are you going to eat with us during the lunch break?’ She responds: ‘yes great, I’ll be right there.’
The rules of the examples listed above are as follows:
- Offensive -> defensive
- Following -> leading
- Defensive -> offensive
- Leading -> following
Rose of Leary – complementarity Theory
Timothy Leary assumes with the rose of Leary that people tend to respond with complementary behaviour to behavioural variants, in which one type of behaviour triggers another type of behaviour.
On the one hand this has to do with the human instinct; on the other hand this has to do with influences from the environment.
In his complementarity theory of the rose of Leary, he indicates how this works:
Above behaviour triggers Below behaviour
Unconsciously we are inclined to respond submissively to above behaviour and we let ourselves be guided and controlled by this.
Below behaviour triggers Above behaviour
Unconsciously we are inclined to display leadership behaviour when we interact with people who display below behaviour, we are inclined to take them by the hand and control them.
Opposed behaviour triggers Opposed behaviour
Unconsciously we are inclined to react more critically when someone else is critical and we are even inclined to agree with so-called defiant behaviour.
Together behaviour triggers Together behaviour
Unconsciously we are energized by working together in harmony. It stimulates us to continue doing our work and to listen to other people’s opinions.
It is only after becoming aware of the complementarity theory, that it is possible to resist this unconscious control. Timothy Leary provides points of reference but he also emphasized that each person responds differently.
The best application for each behavioural variant is to use the opposed variant above-together. Without putting the emphasis on dominance, this behaviour adopts leadership soft skills so that cooperation can be achieved.
By giving the right feedback people, who are inclined to display above behaviour, opposed behaviour or below behaviour, can be corrected and encouraged to cooperate with each other.
Rose of Leary in education
American psychologist Timothy Leary‘s ‘Leary’s rose’ model proved to be very useful in education.
Behaviour can be predicted, to a certain extent, which is what the model is all about. It is also clear that some behaviours evoke other sets of behaviour. The way in which a reaction is given can therefore be predicted and also influenced.
This is valuable in education, where teachers must teach the material to the students with the greatest possible precision.
Leary’s Rose helps to analyse certain behaviours and learn to understand the other person. It can be applied from teachers to students, but teachers can also use the method to analyse their own teaching methods.
Based on this, the teacher can take action when necessary. The method also helps teachers to provoke certain desired behaviours in students.
Rose of Leary test
Toolshero offers you a quick self-test to identify your personal style preference. Use Rose of Leary test as an indicator, and focus on gaining more insights into your own way of communicating. Download the test below, fill in the questions, and fill in the scores on the score card to determine your preferred personal style.
Download the Rose of Leary test
This template is exclusively for our paying Toolshero members. Click here to see if a membership is something for you!Rose of Leary summary
Psychologist Timothy Leary distinguished human behaviour based on four types of behaviour. These are subsequently subdivided. The model in which he has presented his findings is known as Leary’s rose. The tool has proven to be very effective, especially in education.
The communication model in which Leary’s rose is incorporated has a horizontal and a vertical axis as a base. Leary describes the lower behaviour on the southern axis and the upper behaviour on the northern axis. The total is shown in the image at the top of this page.
It’s Your Turn
What do you think? Is the Rose of Leary applicable in today’s modern companies and people development tools? Do you recognize the practical explanation or do you have more suggestions? What are your success factors for self analysis and team development tools?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Leary, T. (1957). Interpersonal diagnosis of personality. The Ronald Press.
- Susilo, A. P., Vv, E., Jv, D., & Scherpbier, A. (2013). Leary’s rose to improve negotiation skills among health professionals: Experiences from a Southeast Asian culture. Education for Health, 26(1), 54.
- Van Dijk, B. (2008). Influence others, start with yourself. About behaviour and Leary’s Rose. Thema.
How to cite this article:
Mulder, P. (2012). Rose of Leary. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/communication-methods/rose-of-leary/
Original publication date: 05/04/2012 | Last update: 11/14/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/communication-methods/rose-of-leary/”>Toolshero: Rose of Leary</a>












