Competency Management: Definition and Tools

Competency Management: this article describes Competency Management in a practical way. Next to what it is (definition), this article also highlights it’s relation with the Business Strategy, the process, a step-by-step plan and it’s relation with career policy. After reading you will understand the basics of this essentieel human resources tool. Enjoy Reading!
What is competency management?
Without employees, organisations are unable to function. It is important to have well-trained and motivated employees who are fully committed to performing their tasks.
For every position, employees require specific competencies; qualities they need in order to perform their work well. In most cases, they are already in possession of these qualities.
Competency Management definition
At the same time, there are also many possibilities for developing various competencies. This is exactly what this human resources discipline is all about. When developing their competencies further, employees will be able to perform their tasks even better.
This will ultimately benefit the company. Many companies engage in competency management because it allows them to align business objectives with the knowledge, skills, and professional attitude of their employees. If it is clear what competencies are required, companies may adjust their recruitment policy accordingly.
Competency management and the Business Strategy
Competency management ensures that there are common values within an organisation’s business strategy. As soon as employees know what expectations they have to meet, this will affect their performances.
In addition, competencies may be readdressed during performance appraisal and career interviews etc. By pointing out employee qualities in concrete terms, they will understand exactly how to improve themselves.
Competency management is all about building and exploiting employee competencies. However, this must always be in line with the strategy and objectives of the organisation, allowing both the organisation and employees to develop together.
An organisation can only flourish once it is clear which competencies employees must possess. Only then can this be taken into account in the recruitment policy and can employees with the right competencies be selected.
In job interviews, the focus will be on knowledge, skills, and characteristics of the candidate. What does he know? What training has he followed? How is he able to apply his knowledge? How competent is he? What experience does he have? What about his solution-oriented skills?
Finally, one must also evaluate the candidate’s general attitude; what is his character and will he fit with the team? Once organisations have defined such core competencies, it becomes easier to integrate them into the entire business strategy.
Talent is a Business Priority and Inbound Recruiting can help
Competency management process, a step-by-step plan
Competency management forms more or less the foundation of a coherent structure and application of the human resources department.
Competency management can be implemented in various ways. The following step-by-step plan is a useful guide:
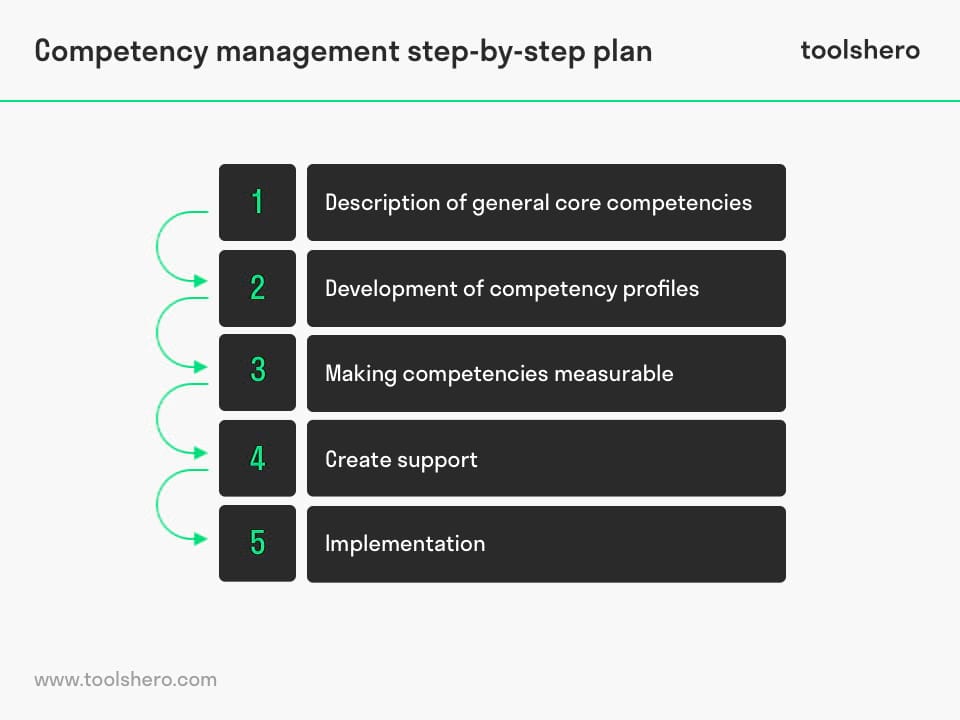
Figure 1- Competency management process, the steps
1. Description of General Core Competencies
By first determining which core competencies are important, the organisation can create a general portfolio of the people it’s looking for. What is the company’s core business, how does it distinguish itself from competitors, and how does the company aim to profile itself to the outside world?
This step is at the strategical level, and revolves around the question of which core competencies are required to remain successful in the coming years.
For instance, an airline company will place great importance on competencies such as customer focus, service-oriented, solution-oriented, and communication. These are the competencies required of employees in every department and within all business units.
2. Development of Competency Profiles
Once the core competencies are clear, one can start determining the competencies of the individual employee. Naturally, these must be derived from the core competencies.
Each department requires specific knowledge, skills and professional attitudes. In the same airline company, technical and analytical insight will be important among the technical staff, whereas stress-resistance will be considered one of the core competencies for the cabin crew.
If job-oriented competencies are not yet clear, it may help to establish profiles on the basis of interviews with managers and employees.
Moreover, the established competency profiles may be added to the job descriptions. A complete list of competencies may also be included in a competency handbook as a useful way to contribute to competency management.
3. Making Competencies Measurable
Once it is clear which competencies apply to the various positions within an organisation, it is recommended to make these competencies measurable. Competencies may be linked to result areas and performance indicators.
This will take place at department level (tactical level), and it is the task of managers to clearly communicate this to their employees. By indicating in advance what is required of employees and how individual competencies are measured, everyone will know what is required of them.
This is made even clearer on the basis of SMART goals; what are the Specific expectations, how is it Measurable, is it Acceptable and Realistic, and what is the Time frame?
For example, based on the number of complaints handled, this approach allows the airline company to evaluate how customer-oriented an employee has been in handling complaints during the past year.
4. Create Support
Regular employees will not necessarily like it if only management and middle management are in charge of determining the competency profiles. They’ll get the impression that all the decisions are made for them.
By involving employees in drawing up the competency profiles, they will be more inclined to take these competencies to a higher level. Competency management will only be successful by creating support among employees.
In addition, employees must understand its usefulness. In the event of any resistance, it is the task of management to conduct individual conversations with employees.
5. Implementation Competency Management
Ultimately, all competencies must be integrated into the human resources policy. The implementation of competency management is only a fact once it has become part of the corporate culture.
At the operational level, the competencies will then form the basis of both the selection process and development process of current staff. Competency profiles are implemented and used during assessment, performance, and personal development interviews, as well as during general job interviews.
Competency management and career policy
Competency management also offers a practical tool for career guidance. In addition to the skills and knowledge of employees, it is also about their personality and behaviour.
To what extent does each employees have the right professional attitude and to what extent are they willing to continue to develop and train? In competency management, it is about recognising, using, and developing the competencies of all employees.
This is in line with the aforementioned business strategy and objectives, and a means to develop cohesion within the organisation.
In this way, employees can be directed based on their attitude. Competencies are based on the future rather than the past, and are focused on employees’ newly acquired skills. Competency management provides clarity and allows employees to function independently.
It’s Your Turn
What do you think? Do you recognize the above practical explanation about competence management or do you have any additions? What are your experiences with building and exploiting the competencies of employees? Do you have any useful tips to share with other readers?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Draganidis, F., & Mentzas, G. (2006). Competency based management: a review of systems and approaches. Information management & computer security, 14(1), 51-64.
- Homer, M. (2001). Skills and competency management. Industrial and Commercial training, 33(2), 59-62.
- Palan, R. (2007). Competency management. Jakarta: PPM.
- Unknown. (2024). HubSpot’s Guide to Choosing a Recruitment CRM for Your Business. Retrieved 01/07/2024 from HubSpot: https://www.hubspot.com/products/crm/recruiting.
How to cite this article:
Mulder, P. (2019). Competency Management. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/human-resources/competency-management/
Original publication date: 06/18/2019 | Last update: 01/07/2024
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/human-resources/competency-management/”> Toolshero: Competency Management</a>












