EPRG Framework (Perlmuter)

EPRG Framework: this article explains the EPRG Framework in a practical way. After reading, you’ll understand the basics of this powerful marketing tool.
What is the EPRG Framework?
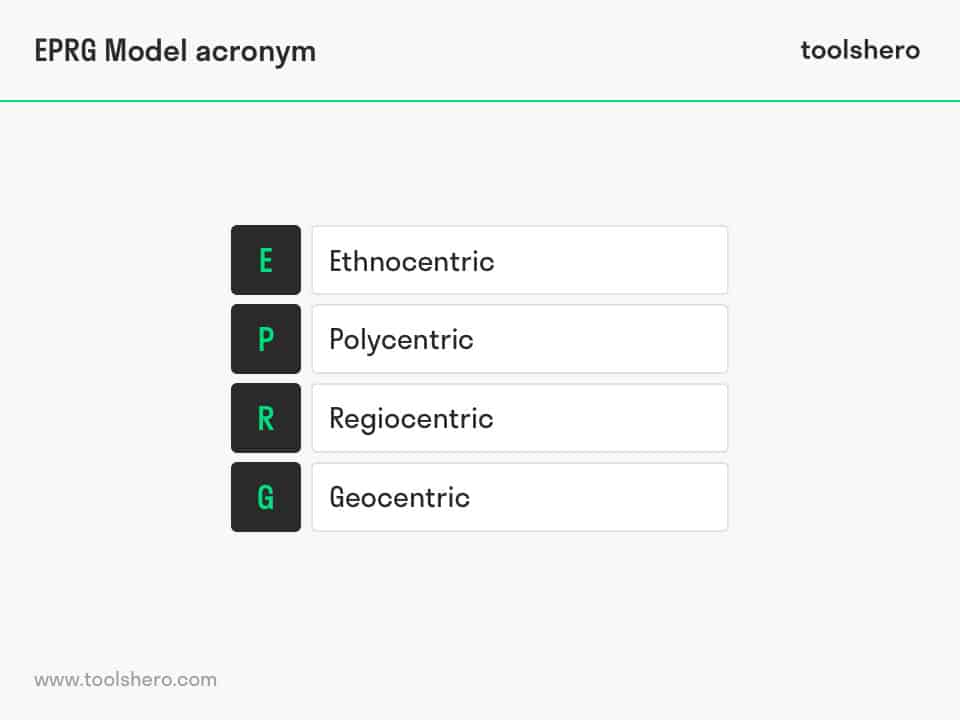
EPRG stand for Ethnocentric, Polycentric, Regiocentric, and Geocentric. It is a framework created by Howard V Perlmuter and Wind and Douglas in 1969.
It is designed to be used in an internationalization process of businesses and mainly addresses how companies view international management orientations. According to the EPRG Framework (or the EPRG Model), there are four management approaches that an organization can take to get more involved in international business substantially.
The EPRG Framework suggests that companies must decide which approach is most suitable for achieving successful results in countries abroad.
For this reason, the EPRG Framework can be a useful tool to utilize if a company does not know yet how to manage business activities between companies in the local country and a host country. The EPRG Framework is additionally useful for making strategic decisions.
In the following section of this article, the four approaches of the EPRG Framework (Ethnocentric, Polycentric, Regiocentric, and Geocentric) are described more in detail.
EPRG Framework approaches
Ethnocentric
In this approach of the EPRG Framework, the company in a local country that wants to do business overseas does not put in much effort to do research abroad about the host country’s market. Instead, most of the market research is executed in the headquarters in the local country.
With this approach, the company seeks for markets abroad that share the same characteristics as the local market so that the marketing strategy does not have to be adapted. More specifically, the ethnocentric approach uses the same marketing strategies that are created by local personnel and further utilized multiple countries.
It is many times possible that companies that utilize this approach believe that local products should not be adapted to the local need of countries abroad because the products are already of high quality. Another reason could be that a specific product is sold in large volume in the local market, and for this reason, it is believed it will do the same in other markets abroad.
The ethnocentric approach of the EPRG Framework has benefits but also downsides. At first, the company saves a lot of operational costs that can be invested elsewhere. But the downside is that the company does not build up new knowledge about the market abroad, which could substantially increase sales volume if products and strategies would be adopted to the needs of the host country.
Polycentric
In the polycentric approach of the EPRG Framework is the opposite of the ethnocentric approach. A company that utilizes this approach carefully consider different markets abroad to identify host countries that could potentially offer the most benefits.
It means that if a company has a local headquarter and a separate office overseas in a host country that manages the operations in that or more countries, the marketing strategies are locally created and implemented based on the local needs.
Businesses that utilize the polycentric approach of the EPRG Framework strongly believe that every market has its differences. For this reason, these types of companies implement different marketing strategies for each market.
In the polycentric approach, it is therefore easier to make strategic decisions based on current cultural differences and political differences. Companies that use this approach can also more easily adapt to changes in the market because of their decentralized decision-making authorities.
The downside is that the local headquarter has less control over its operations abroad. As long as the business operations in the host country demonstrate to be successful, this might not be a problem. But if the business operations overseas show to be not too profitable and result in losses, it is more difficult for the local company to minimize those losses.
However, companies that use this approach learn by doing. For this reason, a learning effect occurs, and new knowledge is an intellectual asset of the company.
If a company is the first to enter a market or offer an unfamiliar product, the local company has first-mover advantages. It could have the best location in a host country to operate the business, and this could additionally substantially increase profit margins.
Regiocentric
In a regiocentric approach of the EPRG Framework, businesses create and implement internationalization strategies for specific regions. Companies that utilize this type of approach use this for the area in which the local business is operated.
It can also be that an organization utilizes two kinds of approaches. An organization can use a regiocentric approach for the business in the region in which it operates. And the same organization can use a polycentric or ethnocentric approach to do business in countries outside the region.
Businesses that use a regiocentric approach of the EPRG Framework many times believe that the markets in the region share the same characteristics of the market in the home country.
It is still challenging to determine countries in one region that share the same characteristics. Consider, for example; some companies use this approach for NAFTA countries, which include the United States, Canada, and Mexico.
All countries are in the same region but still have some different characteristics. The same implies for the Benelux, which include Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg. The countries are in the same region, but Belgium has different market characteristic than the Netherlands and Luxembourg.
The reason why companies use this approach to group countries into for example NAFTA and Benelux. is depending on the type of industry and product or service. Every organization has its way of internationalization.
Geocentric
A geocentric approach of the EPRG Framework means that a business strongly believes that it is possible to utilize one type of strategy for all countries, regardless of the cultural differences.
However, companies that use this approach attempt to create products or offer services in a way that best suit national and international customers. This means that instead of believing that their product or service is excellent and that it will sell in other markets, like in the ethnocentric approach, these organization proactively adapt their products and services that best meet the global needs.
Companies sometimes prefer this type of strategy of the EPRG Framework because it does not involve many adoptions, which minimizes operational costs. These companies use one strategy to sell a product or service, and could for this reason, achieve economies of scale.
Organizations that have a geocentric approach are many times considered as key international businesses because these companies utilize a combination of the polycentric and ethnocentric approaches.
It means that organizations with a geocentric approach of the EPRG Framework can identify similar cultural characteristic, and they can convert the different cultural characteristics into mutual characteristics.
EPRG Framework conclusions
Determining which approach to utilize is dependent on the type of business and in which industry it operates. Due to globalization, many companies operate abroad or are willing to do business overseas. However, doing business abroad really depends on the size of the company and the experience they have.
Even if a business does not know yet what type of approach of the EPRG Framework / EPRG Model is most suitable to the current position of the company, it is always good to research potential markets in term of what size, characteristic, and similar available products in the market.
There is a lot to learn from competitors. This knowledge is free, and it could help to identify what opportunities are available, and thus, which approach of the EPRG Framework is best for an internationalization process.
Now It’s Your Turn
What do you think? Do you recognize the explanation about the EPRG Framework or is this the first time you heard of the model? Are you already doing business abroad or do you want to do business in other markets? Which approach is most suitable for your company? Do you have any tips or additional comments?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Albaum, G., Tse, D. K., Hozier Jr, G. C., Baker, K. G. (2003). Extending marketing activities and strategies from domestic to foreign markets. Journal of Global Marketing, 16(3), 105-129.
- Kumar, V. (2000). International marketing research (pp. 225-226). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Miocevic, D., Crnjak-Karanovic, B. (2012). Global mindset–a cognitive driver of small and medium-sized enterprise internationalization: The case of Croatian exporters. EuroMed Journal of Business, 7(2), 142-160.
- Moses, C., Moore, K., Pleasant, J., Vest, D. (2011). Adapting the EPRG paradigm to internationalizing business schools: A conceptual framework. International journal of business and social science, 2(23).
- Richter, T. (2012). International marketing mix management: Theoretical framework, contingency factors and empirical findings from world-markets. Logos Verlag Berlin GmbH.
- Sandberg, B., Hansén, S. O. (2004). Creating an international market for disruptive innovations. European Journal of Innovation Management, 7(1), 23-32.
- Shoham, A., Rose, G. M., Albaum, G. (1995). Export motives, psychological distance, and the EPRG framework. Journal of Global Marketing, 8(3-4), 9-37.
- Wind, Y., Douglas, S. P., Perlmutter, H. V. (1973). Guidelines for developing international marketing strategies. Journal of Marketing, 37(2), 14-23.
How to cite this article:
Zeeman, A. (2019). EPRG Framework (Perlmuter). Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/marketing/eprg-framework-perlmutter/
Published on: 14/03/2019 | Last update: 05/20/2022
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/marketing/eprg-framework-perlmutter/”>Toolshero: EPRG Framework (Perlmuter)</a>