RATER Model of Service Quality

RATER Model of Service Quality: this article explains the concept of the RATER Model of Service Quality, developed by Valarie Zeithaml, A. Parasuraman and Leonard Berry in a practical way. This article also highlights, next to what is, it’s relationship with the SERVQUAL Model and the GAP Analysis. After reading it, you will understand the basics of this Marketing tool. Enjoy reading!
What is the RATER Model of service quality?
Commercial businesses like to be able to assess in advance what their customers expect from the product and / or services they buy.
The RATER Model is a convenient method to measure customer expectations. It was created by Valarie Zeithaml, A. Parasuraman and Leonard Berry for service quality.
They first mentioned the RATER Model of service quality in their book ‘Delivering Quality Service’ from 1990. Companies can use the RATER model to improve their individual services. They need customer information that they can obtain using the this model.
The RATER Model of service quality is the result of further refinements within the SERVQUAL Model. After carrying out several tests, the designers of the model concluded that there were overlaps within the dimensions of the SERVQUAL Model.
Where the SERVQUAL Model works with 10 dimensions to measure the quality of service, the RATER model works with 5 dimensions.
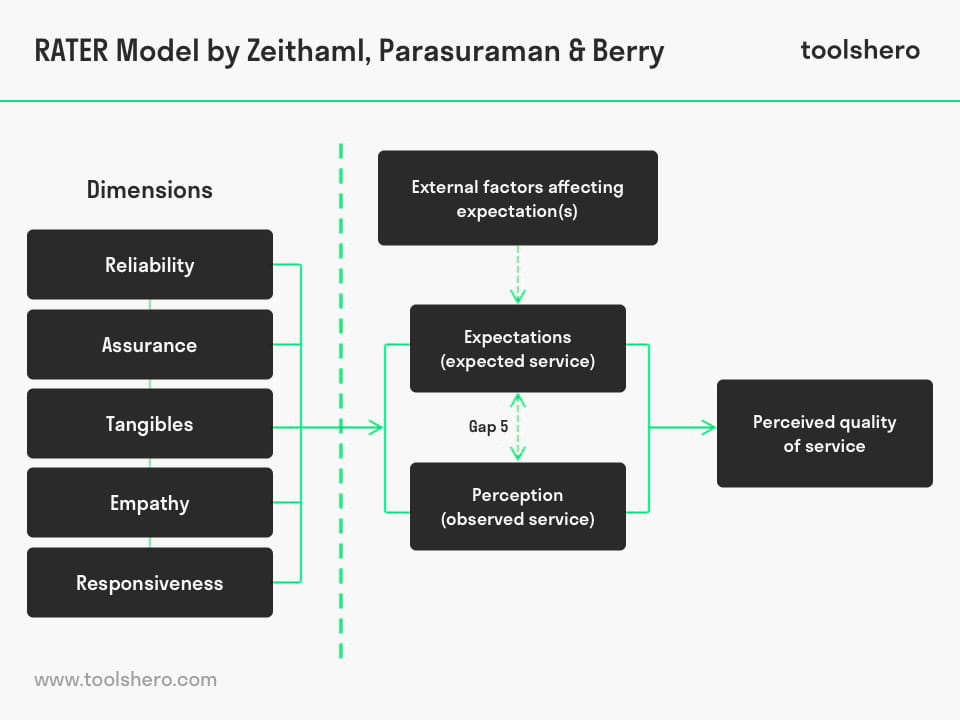
Figure 2 – SERVQUAL Model versus RATER Model
The model emphasises 5 areas that customers generally deem important when they use services such as education, energy, telecommunications, banking, insurance, air travel, transport etc.
The model focuses on the difference between customer experiences and customer expectations. RATER is an acronym of five factors: Reliability, Assurance, Tangibles, Empathy and Responsiveness. All five factors are explained below.
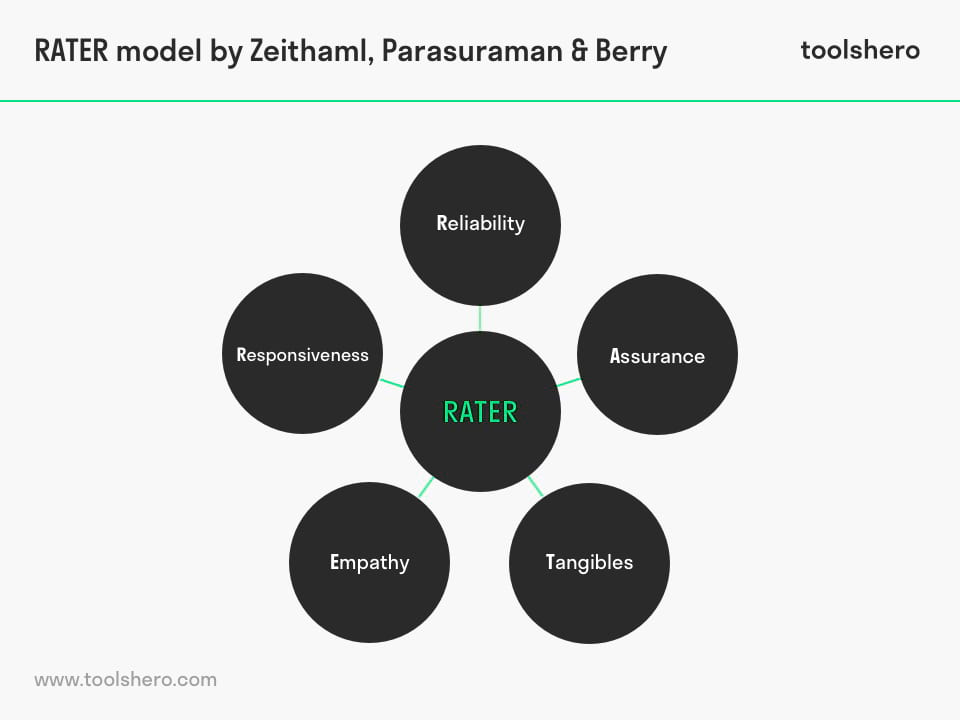
Figure 1 – RATER Model (Reliability, Assurance, Tangibles, Empathy and Responsiveness)
Reliability
Is the organisation able to deliver the agreed upon services consistently, accurately and on time? This concerns the quality of the reliability and the way in which the customer can rely on it. If it turns out that a provider is not able to deliver Internet services without issues, the organisation’s reliability will decline.
Assurance
Are employees able to convincingly communicate their knowledge to the customers? Does the customer trust what the employees have to say and do they feel the employees can give them helpful advice? When the information about an interest tax deduction for an expensive mortgage turns out to be inaccurate, both the bank’s and its employee’s credibility will diminish rapidly. The customer might even go to a different bank for his mortgage.
Tangibles
Are the physical aspects of the service appealing? Think for instance of the office, website, equipment and employees looking reliable.
If a customer is selecting a health insurance plan, but ends up on a website that looks unprofessional, that customer will probably opt for a different insurance company.
Empathy
Are employees able to empathise well with the customers and give them individual attention? How is the relationship between employees and their customers? If a customer has a complaint about a considerable delay at an airline, he wants to feel heard by the employee. If there is not even a shred of empathy in the employee’s response, the customer will be disappointed and decide never to fly the airline in question again.
Responsiveness
To what extent can the organisation offer quick service and to what extent is the company willing to help customers? Quality service is paramount. If a commercial training institute does not pay enough attention to a customer who requested more information about a specific study programme, chances are the customer will look for a different school.
After all, the customer wants to start the programme within a month. If it takes a month just to get a response, he is likely to have found another study programme.
Improvement by the RATER Model
If the customers had expected more from the service than they actually experienced, they will have a low opinion of the service quality. By measuring this quality rating using the 5 RATER areas, an organisation can discover where opportunities for improvement lie. A multi-dimensional approach allows the service shortcomings to be identified and improved.
RATER Model and the GAP Analysis
The RATER method is based on the idea that customers rate the quality of a service provider by comparing their experiences to their expectations.
A GAP Analysis can then measure the gap between experience and expectation, making it clear to the company ‘where they are and where they want to go’.
That kind of analysis is applied to each of the five RATER areas. The eventual goal of the process is addressing the gaps.
Quality control and process improvement can only be implemented after finding out what the customers think. A company can focus on improvement in the areas where the customers’ expectations are different from the actual offered quality.
It’s Your Turn
What do you think? What is your experience with the RATER Model of Service Quality? Do you recognize the practical explanation or do you have more suggestions? What are your success factors for measuring customer expectations?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Czaplewski, A. J., Olson, E. M., & Slater, S. F. (2002). Applying the RATER model for service success. Marketing Management, 11(1), 14.
- Grapentine, T. (1998). The history and future of service quality assessment. Marketing Research, 10(4), 4.
- Iacobucci, D., Ostrom, A., & Grayson, K. (1995). Distinguishing service quality and customer satisfaction: the voice of the consumer. Journal of consumer psychology, 4(3), 277-303.
- Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. L. (1985). A conceptual model of service quality and its implications for future research. the Journal of Marketing, 41-50.
How to cite this article:
Mulder, P. (2018). RATER Model of Service Quality. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/marketing/rater-model/
Original publication date: 02/06/2018 | Last update: 02/23/2024
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/marketing/rater-model/”>Toolshero: RATER Model of Service Quality</a>