Perceptual Positions technique

Perceptual positions technique: this article provides a practical explanation of the perceptual positions, a NLP exercise. Next to what it is, this article also highlights perceptual positions technique and positions, the process step by step explained and the sensation experience. After reading, you’ll have a basic understanding of this NLP technique. Enjoy reading!
What are the perceptual positions?
We all have at least one of those negative experiences, situations, or events that stays forever engraved in our memory. Even if it’s a long time ago, it can still cause a certain annoyance when talking about it.
In that case, it’s impossible to look at the situation from a different angle because the emotion evoked by that memory is negative.
Perceptual positions can be very useful here. This is an exercise from Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP). It is a reframing exercise; by ensuring that someone can look at a situation from three different perceptual positions, they can gain insight by means of three different perspectives.
From these triple positions, a person can distance themselves from emotionally-charged situations or events. It can also be used to foster empathy for the other person and to gain valuable insights into how someone else perceives a situation.
It provides the ability for one to see things from another person’s point of view. This is a skill in understanding people and is important for communication processes in relationships and negotiation.
Perceptual positions represent a profound contribution to the study and practical applications of the human mind. Another person can only be understood when the situation has been looked at from their perspective and it becomes clear what their experience was.
Perceptual positions technique and positions
Perceptual positions include the 1st position (I), the 2nd position (the other), and the 3rd position (the observer), also called the Meta Position. The usefulness of these perceptual positions is that someone receives insight into how someone else looks at a situation and realises that their own experience may be biased.
In this way, someone gains more information about themselves and others. By looking at a situation from the three different positions, listening and experiencing, one learns to discover things which one wasn’t aware of before.
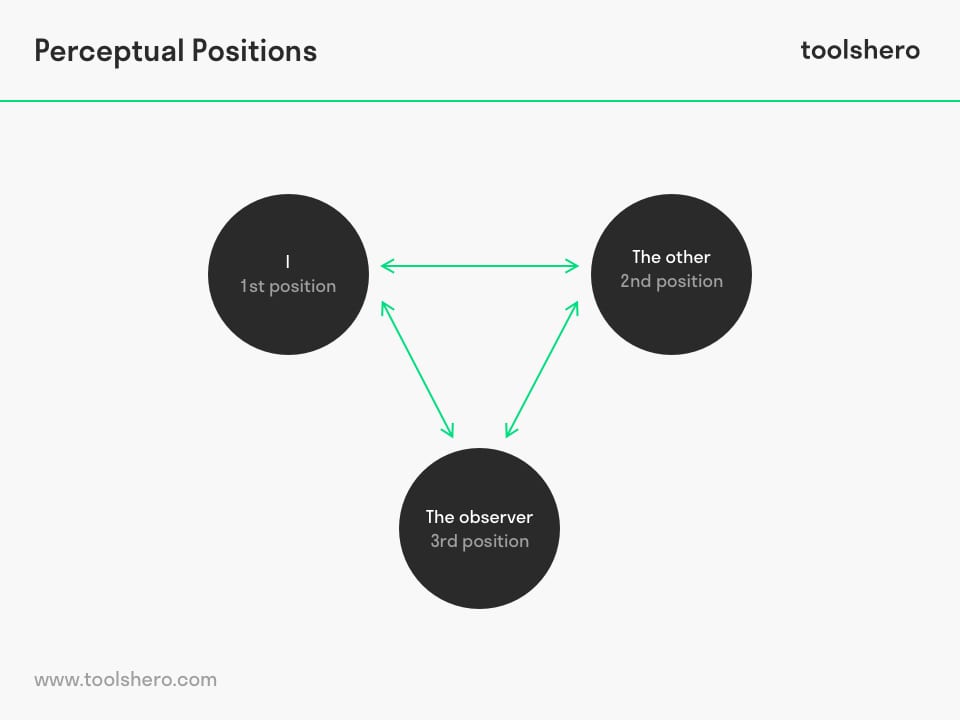
figure 1 – Perceptual Positions process, the three perspectives
The three possible perspectives perfectly demonstrate the interaction between oneself and others.
NLP includes visual representation, but also kinaesthetic, auditory and, to a lesser extent, olfactory and taste systems. It is therefore the intention that one fully associates with one of the perceptual positions at all times during the exercise and to use all the senses in doing so.
In the first position, someone thinks, feels, does, sees, hears, smells, and tastes entirely from within oneself. In the second position, someone thinks, feels, does, sees, hears, smells, and tastes as if they are the other person entirely. They place themselves in the other person’s shoes.
In the third and final position, someone becomes the independent outsider. As an objective observer, who is not involved in the situation, this person observes:
1st position
First of all, the situation must be seen, heard, and felt by our own filters. One’s personal experience is key. The more the body feels physically and emotionally, the clearer the 1st position feels.
Within NLP, this is called the ‘fully-associated position’; someone experiences the situation again and sees everything crystal clear in front of them. It’s like travelling back in time and so requires great concentration. It provides interesting insights.
2nd position
In the 2nd position, it is the intention that someone sees, hears and feels the same situation as in the 1st position through the other person’s filters.
This position can be in direct communication with the 1st position. This position is associated with impressionists: salespeople, therapists, and coaches are able to empathise with one another and see the world through the other’s eyes.
3rd position
The final idea is to see, hear, and feel the situation through an observer’s filters, the so-called ‘fly on the wall’, who watches without judgement.
In this objective perceptual position, it is as if one were watching the situation unfold on the silver screen. From this 3rd position, someone poses as an interested but not directly involved observer. Possible emotional charge is omitted. The bigger picture can be viewed in a single glance. This person is the ‘friendly visitor from space’. In this way, this 3rdposition is suitable for one assuming the role of ‘own coach’.
Perceptual positions process, step by step
It’s very easy to apply the perceptual positions according to the following step-by-step plan:
Step 1 of the Perceptual Positions technique
One takes a difficult conversation or situation into consideration. Perhaps the people in the conversation do not get along well with each other. It is important to sit upright or stand with your shoulders back.
By focusing on the situation, someone hears themselves talking again, knows what they did, how they reacted, and how they felt at that moment. While visualisation of the process takes in the first step, it is important to reflect on conspicuous points and to ask why this happened.
Step 2
After taking the time for the first step (1st position), the person will look at the situation from the other person’s perspective in the same way.
By describing the situation now, it becomes clear how the other person saw the other person, how he felt, and what he did. Again, it is important to reflect on discoveries and to find out why the other person reacted in a certain way.
Step 3
Now the time has come to look at the situation from the 3rd position and to observe the two people as it were. One may wonder what is striking about the situation one sees and what the intentions of both people in the conversation are.
How could the two of them come to a joint solution and how is it that their conversation is difficult? From the 3rd position of the perceptual positions, one is able to give oneself wise advice.
Step 4
This is the step where someone starts reflecting on the exercise. One can ask oneself which position was easiest to take.
Since the previous steps always looked at conspicuous points, new information comes to light that someone was not aware of at first. This can change the understanding of the situation and cause someone to make different choices and to approach the person they’re talking to differently next time.
Sensation
The sensation that one experiences in all positions is crucial in finally going through step 4. This sensation offers new insights into oneself, the other, and the situation.
Analysing the situation is only possible by re-experiencing the previous experiences from the three different positions. Nevertheless, one of the three positions can also be emphasised. If someone is looking for more empathy, for example, they can dwell longer on the 2nd position.
If an objective view is important, then the 3rd position is considered to be the most dominant. Perceptual positions are about increasing the number of choices in human life through the three positions.
Now it’s your turn
What do you think? Do you recognize the explanation of the perceptual positions technique? What insights has this given you? Are there any tips or additions you would like to share?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Andreas, C., & Andreas, T. (2009). Aligning perceptual positions: A new distinction in NLP. Journal of Consciousness Studies, 16(10-11), 217-230.
- Grimley, B. (2007). NLP coaching. Handbook of coaching psychology: A guide for practitioners, 193-210.
- Slater, M., & Usoh, M. (1993). Representations systems, perceptual position, and presence in immersive virtual environments. Presence: Teleoperators & Virtual Environments, 2(3), 221-233.
How to cite this article:
Mulder, P. (2019). Perceptual Positions technique. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/personal-development/perceptual-positions/
Published on: 01/10/2019 | Last update: 08/15/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/personal-development/perceptual-positions/”>Toolshero: Perceptual Positions technique</a>












