Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)

Failure Mode and Effects Analysis: this article provides a practical explanation of the Failure Mode and Effect Analysis or FMEA. After reading this article, you will understand the basics of this powerful quality management and risk analysis tool.This article also contains a downloadable and editable excel FMEA template.
What is FMEA / Failure Mode and Effect Analysis?
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis or FMEA is an analysis tool used to map various possible risks in a process. The methodology is used to determine the chance of failure and the ensuing risks in developmental processes of services, products or production methods.
The goal of the Failure Mode and Effect Analysis or FMEA is to define actions that reduce the chance of failure. The multidisciplinary aspect of this tool ensures that a complete image is shaped regarding the quantifiability of risks. This means a hierarchy can be applied in the urgency of the risks. A useful tool that can help to do this is the Risk Analysis Tool.
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis or FMEA has its origin in an environment where the interests to reduce risks are extremely large: The National Aeronautics & Space Administration (NASA). Around 1960, NASA used this analysis model in the Apollo missions. In the decades after, the technique was implemented in the automotive industry and food industry. Nowadays, the Failure Mode and Effect Analysis or FMEA can be applied in practically any process analysis and a large number of variations are available.
Types of Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis or FMEA can be used in countless situations and circumstances. The most frequently used applications of FMEA are:
Design FMEA (DFMEA)
The Design FMEA is used to identify potential risks in the design of a product or service. Initially, the Design FMEA identifies design functions, error modes and the effects on the customer.
Process FMEA (PFMEA)
The Process FMEA is used in the analysis of possible errors and risks in an organisational process. First, the Process FMEA identifies process functions, failure modes and the effects of the errors on the process.
Machine FMEA (MFMEA)
Machine FMEA is a methodical approach for identifying risks that are related to the failure of machines and equipment. The goal of MFMEA is to increase the reliability of machines and shorten the time required for repairs. Machine FMEA identifies the machine functions, work speed and expected productivity.
Healthcare FMEA (FMEA)
Healthcare FMEA is an analysis process that is used to identify potential failures and their causes in hospitals. The goal of the Healthcare FMEA is to increase patient safety. Despite the fact that with each type of FMEA a different organisational component or function is analysed, the basis and method for each type is the same.
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis or FMEA : main elements
The Failure Mode and Effect Analysis or FMEA template can be filled in by means of three criteria. A score between 1-10 can be assigned to each of these three criteria. Subsequently, these scores can be filled in in the formula to calculate the Risk Priority Number (RPN). This is explained in point 4. In an FMEA, the following three criteria are used to evaluate the problem:
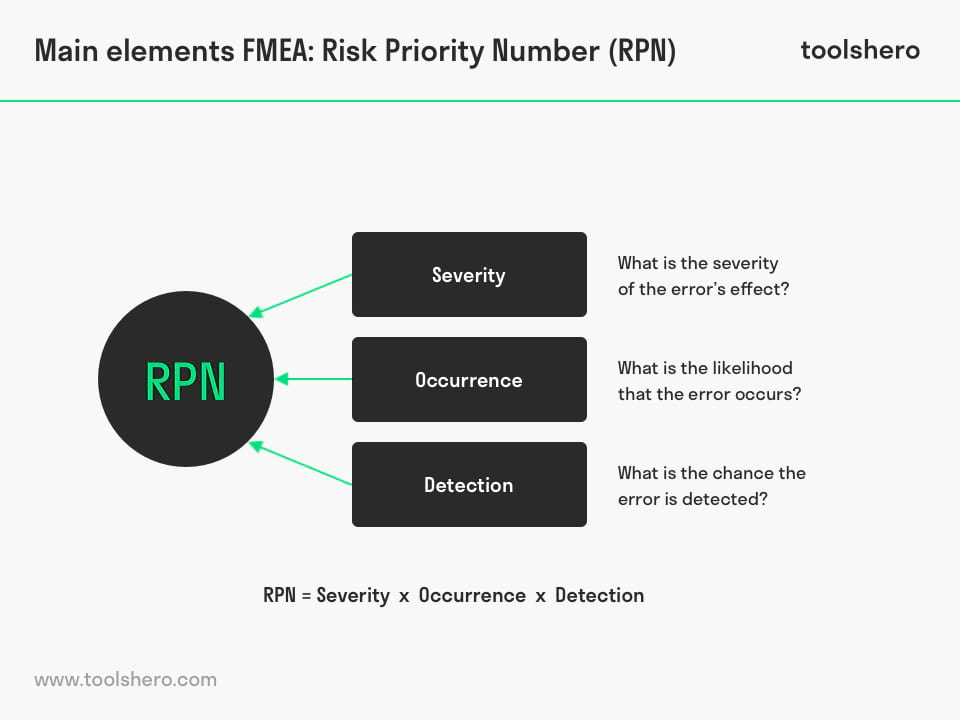
Figure 1- the FMEA elements
1. The severity of the error’s effect (severity)
The priority ranking of severity encompasses what is important for the industry, organisation or customer, such as: safety, environment, production continuity, loss, damaged reputation.
1-4: Minor disruptions that require little alteration and where minor adjustments are sufficient.
5-6: Mild disruptions that require alteration and major adjustments.
7-8: Major disruptions that require a lot of alteration and major adjustments.
9-10: Extreme disruptions where regulations and safety are a concern.
2. The likelihood that the error occurs (occurrence)
This is the ranking of the frequency with which an error occurs during the lifespan of the product or service.
- Preventing through product/process design; error-resistant
- Almost certainly the error is noticed in time
- The error is most likely noticed
- The error will probably be noticed
- Moderate probability that the error is noticed
- Small chance of error detection
- Very small chance of error detection
- Remote chance of error detection
- Very remote chance of error detection
- No chance of error detection. No implemented control mechanisms or procedures are in place to notice the error
3. The chance the error is detected (detection)
Here, the chance the problem is detected before it happens is ranked.
1-2: Extremely high. Errors can almost always be detected. Reliable detection with management elements that are known in similar processes.
3-4: High. Management elements have a good chance of detecting the error modes.
5-6: Average. Management elements detect possible error modes.
7-8: Low. Management elements have a low chance of detecting errors.
9: Extremely low. Management elements will probably not detect errors.
10: No detection. Management elements do not detect errors.
4. Risk Priority Number (RPN)
The Risk Priority Number (RPN) is the value given to the various risks to represent the chance that an error causes a critical failure. The RPN consists of the product of the three aforementioned criteria, each with a maximum score of 10, and therefore has a maximum value of 1000. The lower the score, the lower the risk and vice versa. The formula for calculating the RPN is:
RPN = Severity x Occurrence x Detection
An example of such a calculation of the RPN can be found in the toolshero template
Steps for filling in the FMEA template
- The component that may be subject to a possible error must be written down in column B.
- Column C describes what could go wrong in the act or step described in column B.
- Column D requires a description of the possible effects of the potential error.
- In column E, severity, a score between 1 and 10 is assigned, based on the criteria from the columns B and D (severity).
- If there are procedures/ tests/ mechanisms in place that could have prevented the failure, these will be noted in column F, current process controls.
- The cause of failure, the error, is filled in in column G.
- Column H (occurrence) consists of a score between 1 and 10 based on the criterion from column G.
- In column I, a score between 1 and 10 must be added that represents the probability that the error occurs (detection).
- The Risk Priority Number in column I is automatically calculated after filling in the scores in the columns E, H and I.
- The measures that can be taken to remedy the error or minimise the impact are noted down in column K.
- In column L, the person bearing responsibility for executing the measures in column K is noted down.
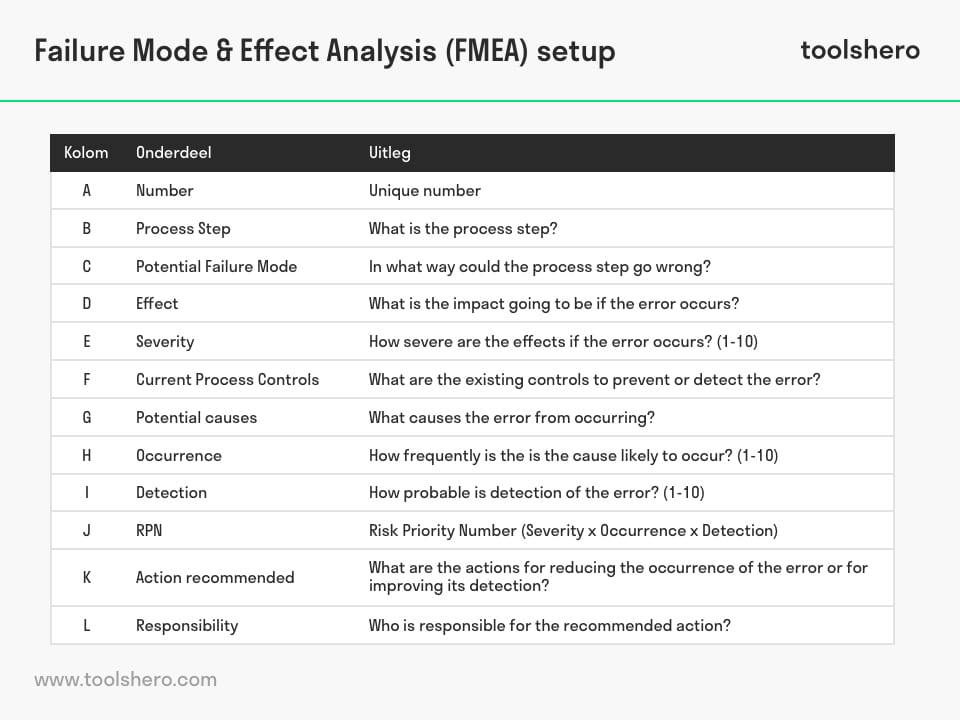
Figure 2 – FMEA setup
Benefits of Failure Mode and Effect Analysis or FMEA
In case of correct use of the FMEA, this method offers various benefits to organisations:
- Increasing product and process reliability
- Increasing product and process quality
- Increasing customer satisfaction
- Early identification and elimination of possible process and product disruption modes
- Cost reduction for early identification and elimination of possible process and product disruption modes
- Prioritising shortcomings in products/processes
- Emphasising the usefulness of problem prevention
- Documents procedures and action plans to reduce future risks
- FMEA works as a catalyst for teamwork and the exchange of ideas between different disciplines
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis / FMEA template
In this FMEA template you can identify risks, consequences and solutions using the FMEA technique.
Download the FMEA template
This template is exclusively for our paying Toolshero members. Click here to see if a membership is something for you!It’s Your Turn
What do you think? How do you conduct the Failure Mode and Effect Analysis or FMEA? Do you recognise the explanation and steps for creating a reliable FMEA or is there anything you would like to add? According to you, what are other success criteria for mapping risks?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- McDermott, R., Mikulak, R. J., & Beauregard, M. (1996). The basics of FMEA. SteinerBooks
- Stamatis, D. H. (2003). Failure mode and effect analysis: FMEA from theory to execution. ASQ Quality Press.
- Franklin, B. D., Shebl, N. A., & Barber, N. (2012). Failure mode and effects analysis: too little for too much?. BMJ Qual Saf, 21(7), 607-611.
How to cite this article:
Janse, B. (2018). Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA). Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/quality-management/failure-mode-and-effects-analysis-fmea/
Original publication date:: 08/16/2018 | Last update: 04/16/2024
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/quality-management/failure-mode-and-effects-analysis-fmea/”>Toolshero: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)</a>













2 responses to “Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)”
Excellent, described very correct and with clear steps..
Thank you.
Well explained FMEA topic with all cons of implementation this method in every process we make.
Need to try that with yours resource