Intervision explained

Intervision: this article offers a practical explanation of intervision. After reading, you’ll understand the basics of this communication tool. This article contains a general definition of the concept of intervision and the various steps involved. Enjoy reading!
What is intervision?
Intervision is a form of knowledge development in a small group of professionals, managers, or other employees who share a common challenge or problem.
Professionals and colleagues can consult the expertise of others to help them gain valuable new insights. The ideal group consists of about five to eight participants. Together they dissect a problem that has been introduced by a participant or so-called case provider. They do so by asking questions using the intervision method.
Intervision is not primarily intended to solve a problem, instead the group encourages each other to find answers by asking questions. These questions should help the case provider develop a new way of thinking in order to gain insight into their problem or question.
Intervision can also take place on a personal level. It can be about dealing with problems at work, problems with an approach, or other types of problems.
Intervision is always tied to something from day-to-day practice, professionalisation and improvement, and learning and development. It makes the person involved aware of individual styles and preferences, their personal view on the work, and the way in which work is handled.
The Value of Intervision for Organisations
If intervision is applied in a suitable way within an organisation, it will have a positive impact on the atmosphere in the group.
For instance, it reinforces a sense of solidarity between different employees or even between people in general. It also helps the employee develop an awareness and learn to improve based on experience and intervision sessions.
Intervision helps with the development of so-called learning skills and soft skills:
- Active listening
- Sense of empathy
- Asking good questions
- Creative thinking
- Innovative problem solving
- Improved teamwork
- Solidarity between participants
Intervision Steps
Conducting an intervision session isn’t difficult. Follow the steps below to hold an effective intervision session.
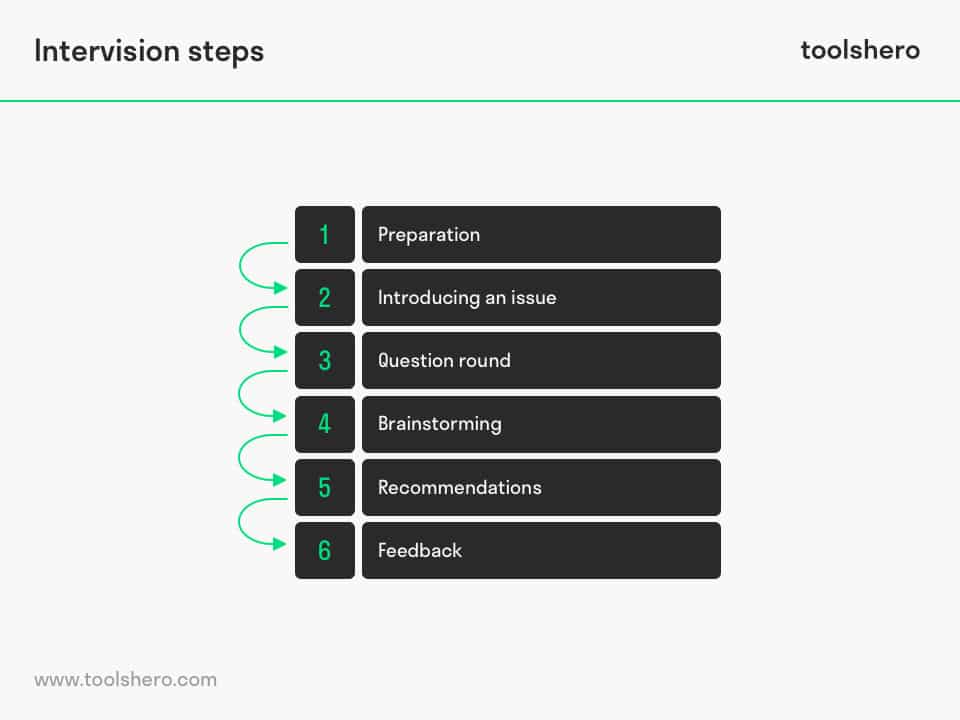
Figure 1 – Steps of the Intervision Process
Step 1: preparation
First it has to be determined where the session will take place, and whether a facilitator will be present. The facilitator leads the session and prevents participants from losing focus. The facilitator also ensures every problem is given an equal amount of time.
There are different ways in which an intervision session can be conducted. One option is that everyone brings a problem or issue to the table.
In this case, the step-by-step plan below will be used for each individual problem. These sessions will take approx. three hours.
Of course, this is pretty long. Moreover, people’s short attention spans will mean that everyone will lose focus after a few problems. It is therefore a better idea to hold a session in which only one or two problems are covered. That way it will take about 20 minutes to half an hour.
The advantage of a short session is that participants will remain relatively sharp, resulting in useful advice.
Step 2: introducing an issue
In the first step, participants (five to eight) share their issue with the group. Each participant is given three minutes to explain their problem or challenge. Make sure it’s a current problem, not one from the past or future.
Step 3: question round
During the second step, participants will ask each other question to clarify certain details and learn more about the topic and problem.
All relevant information that is obtained this way has to be remembered or recorded. Ensure that the information covers the entire scope of the problem, and that participants don’t start discussing possible solutions yet. This will be done in step four.
Step 4: brainstorming
Now that the information has been gathered, it’s time for a brainstorming session. The group will discuss how the problem can be approached from different angles, and potential solutions can be tested in theory.
Use a whiteboard with post-its on which relevant ideas are written down. This visualises different aspects throughout the process.
The person who introduced the issue to the session can listen in, but not take active part in the conversations about the topic.
Step 5: recommendations
Based on the brainstorming session, the participants make and share a list of recommendations to the person with the problem.
It’s important that the advice in this step is concrete, with feasible suggestions and recommendations. The participants should give their recommendations within two minutes.
Step 6: feedback
During this step, the person who introduced the problem will take time to give feedback about the recommendations that have just been made.
It’s important to point out elements that work and actually form a solution to the problem, as well as things that won’t work. This way the persons in the group will keep each other on their toes.
Finally the case provider will summarise the added value of the session and what they will remember for the future.
Different Intervision Session Methods
In addition to the traditional method consisting of the step-by-step plan, there are a few alternative methods to do intervision. The most important ones will be explained here.
Gossip method
The gossip method is a frequently used type of intervision session and works best if the case provider is knowledgeable about the problem at hand. The problem is shared in the group, after which participants ‘gossip’ about what they’ve just heard. The case provider doesn’t participate. Participants are critical about the following matters:
- Impression of the case provider
- Potential involvement of the case provider in the problem
- Cause of the present situation
Although this method is called the gossip method, it’s important that it is conducted in a safe, trusted group with mutual respect. The tone of the ‘gossip’ should be respectful and concrete. The method can be used for anyone and works best with a critical and strong facilitator.
Intervision and the incident method
The incident method is very suitable for use when an incident has taken place to which the case provider has had and still has a strong emotional response.
It focuses on the actions of the case provider. Here it is important that the case provider doesn’t share the outcome of the incident and that the situation occurred recently. In this approach, the group analyses the situation surrounding a problem in detail.
Now It’s Your Turn
What do you think? Are you familiar with this explanation of intervision? Will you be using the step-by-step plan to effectively resolve issues, or do you already use a similar communication tool? Which intervision method do you think will be most effective? Do you have any tips or additional comments?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Lippmann, E. (2004). Intervision. Kollegiales Coaching professionell gestalten, Berlin et al.
- Hendriksen, J. (2002). Intervision: kollegiale Beratung in sozialer Arbeit und Schule. Beltz Juventa.
- Brinkmann, R. D. (2002). Intervision: ein Trainings-und Methodenbuch für die kollegiale Beratung; mit zahlreichen Checklisten. Sauer.
- Franzenburg, G. (2009).Educational intervision: Theory and practice Problems of Education in the 21st Century, 13(1), 37-43.
How to cite this article:
Janse, B. (2019). Intervision. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/communication-methods/intervision/
Published on: 08/02/2019 | Last update: 04/03/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/communication-methods/intervision/”>Toolshero: Intervision</a>












