4 Types of Innovation (Henderson and Clark)

4 Types of innovation: this article explains the 4 types of innovation as described by Henderson and Clark (1990). The article begins with a general introduction and definition of the concept of innovation, followed by an explanation of each type of innovation, including benefits and examples. Enjoy reading!
What is innovation?
Innovation drives progress and propels societies and businesses forward by introducing new ideas, products and processes.
In the field of innovation, there is a renowned framework, proposed by Professors Rebecca Henderson and Kim B. Clark, that identifies four distinct types of innovation. These classifications help us understand the diverse ways innovation manifests itself and its impact on industries.
In this article, we will explore each type of innovation, starting with an example that highlights its essence and importance.
Origin of the framework for types of innovation
The framework developed by Henderson and Clark grew out of their extensive research into innovation practices in various industries. Their work focused on understanding how businesses adapt and thrive in an ever-changing marketplace.
By analyzing numerous case studies and collaborating with industry leaders, they have identified four distinctive types of innovation that capture the essence of successful innovation strategies.
In the following sections, we’ll take a closer look at each type of innovation, exploring their features, benefits, and the role they play in shaping the course of business and society.
4 Types of innovation
Below you will find a general explanation of the four types of innovation as described by Henderson and Clark.
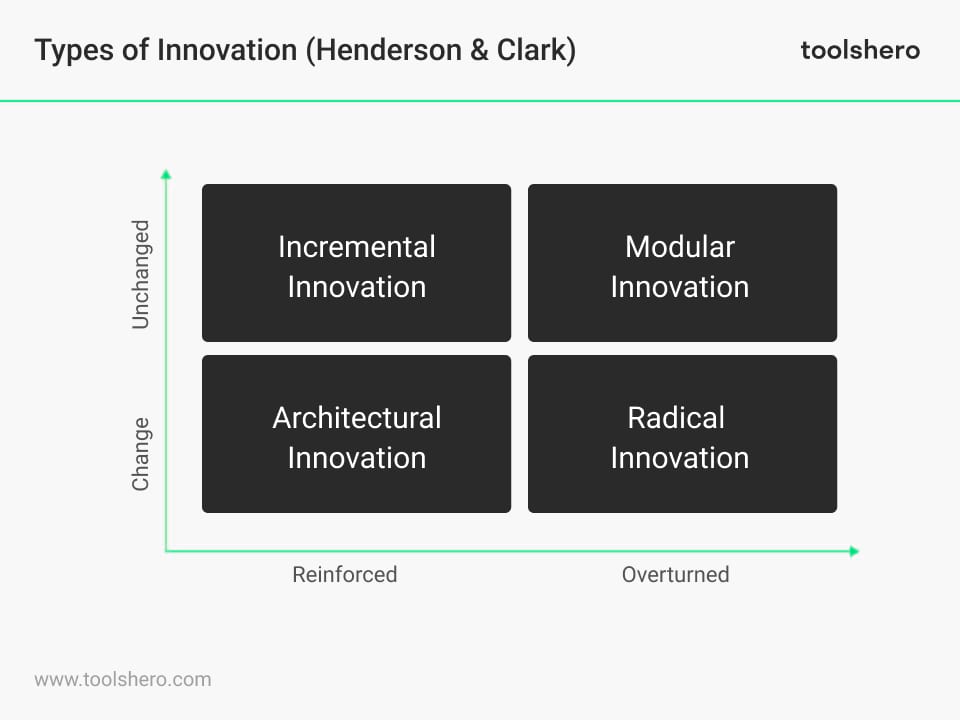
Figure 1 – 4 types of innovation (Henderson and Clark)
Type 1 – Incremental innovation
Incremental innovation refers to small, gradual improvements made to existing products, processes or services. It involves making incremental changes or improvements to improve efficiency, quality or functionality.
Example: The continuous updates and improvements made to popular software applications such as Microsoft Office, with each new version introducing new features, improved user experience, and better performance.
Benefits of incremental innovation:
- Enables continuous improvement of existing products, processes or services
- Minimizes risks, compared to radical changes, making it easier to implement and adopt
- Increases customer satisfaction by addressing incremental needs and preferences
Type 2 – Modular innovation
Modular innovation means developing independent components or modules that can be easily combined or exchanged to create different configurations. It offers flexibility, efficiency and customization options in design and production.
Example: Lego building blocks offer modular innovation where individual blocks can be combined and interchanged to create countless configurations and structures, allowing children to exercise their creativity and imagination.
Benefits of modular innovation:
- Facilitates faster development and implementation of new products or services
- Promotes scalability and customization through modular components
- Strengthens collaboration and innovation by allowing various organizations to contribute to a shared ecosystem
Type 3 – Architectural innovation
Architectural innovation involves reconfiguring the overall design or structure of a product, system, or organization. It involves making significant changes to the underlying framework or architecture to achieve new functionality, performance improvements, or cost efficiency.
Example: Tesla’s electric cars are an example of architectural innovation by integrating advanced battery technology, electric drive systems and software systems.
This integration is revolutionizing the automotive industry by offering sustainable, high-performance vehicles with unique features such as over-the-air updates and autonomous driving.
Benefits architectural innovation:
- Enables the creation of new business models and value propositions
- Improves flexibility and adaptability by uncoupling components within a system
- Drives collaboration and partnership opportunities using modular interfaces
Type 4 – Radical innovation
Radical innovation involves introducing completely new products, processes or business models that significantly disrupt existing markets or create entirely new ones. It is often accompanied by groundbreaking and transformative developments.
Example: The introduction of the Internet and the World Wide Web has revolutionized communication, access to information and the way we do business. This radical innovation has brought about profound changes in several industries, enabling global connectivity, e-commerce and the digital transformation of countless aspects of our lives.
Benefits of radical innovation:
- Holds the potential for disruptive and transformative breakthroughs
- Creates new markets or radically reforms existing markets
- Offers competitive advantage and differentiation by introducing new and unique solutions
Summary on the 4 types of innovation
The Henderson and Clark framework is based on extensive research into innovation practices across industries.
The four types of innovation are:
- Incremental innovation: Small, gradual improvements to existing products, processes, or services. Example: Ongoing updates in software applications such as Microsoft Office.
- Modular innovation: Development of independent components that can be easily combined or exchanged. Example: Lego building blocks.
- Architectural innovation: Reconfiguring the design or structure of a product, system, or organization. Example: Tesla’s electric cars with advanced battery technology and software.
- Radical innovation: The introduction of completely new products, processes or business models that disrupt existing markets or create new ones. Example: the Internet and the World Wide Web.
The different types of innovation each have their own advantages and can have a major impact on industries and societies.
Incremental innovation enables continuous improvement, modular innovation promotes flexibility, architectural innovation drives new business models, and radical innovation creates potentially transformative breakthroughs and new markets.
Now it’s your turn
What do you think? Do you recognize the explanation of the 4 types of innovation as described by Henderson and Clark? Which type of innovation is most common in your sector? What type of innovation do you think is most important for future growth? What hurdles do you think organizations might face in pursuing each type of innovation? Do you have tips or other comments?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Henderson, R. M., & Clark, K. B. (1990). Architectural innovation: The reconfiguration of existing product technologies and the failure of established firms. Administrative science quarterly, 9-30.
- Popa, I. L., Preda, G., & Boldea, M. (2010). A theoretical approach of the concept of innovation. Managerial Challenges of the Contemporary Society. Proceedings, 151.
- Burco, R. A., & Henderson, C. D. (1971). Systems innovations for urban transportation. Transportation Engineering Journal of ASCE, 97(2), 205-226.
- Clark, E., & Webster-Henderson, B. (2012). Innovation and its contribution to the scholarship of learning and teaching. Nurse education today, 32(7).
How to cite this article:
Janse, B. (2023). 4 Types of Innovation (Henderson and Clark). Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/innovation/types-of-innovation/
Original publication date: 09/29/2023 | Last update: 09/29/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=” https://www.toolshero.com/innovation/types-of-innovation/”> Toolshero: 4 Types of Innovation (Henderson and Clark)</a>












