Social Selling Index (SSI) explained

Social Selling: this article provides a practical explanation of Social Selling. Next to what it is (the basics and defintion), this article also highlights Social Selling Index and the four importan pillars of this strategy, the importance of social media groups and social listening. After reading, you’ll understand the basics of this marketing and sales strategy. Enjoy reading!
What is Social Selling? The basics
The definition of social selling
Social Selling refers to sellers using social media to interact with customers directly. Marketing teams share valuable content, sales teams answer questions and subsequently provide interested parties with thorough information, stimulating a potential purchase.
Through interaction and involvement, the potential buyer is supported throughout the entire sales process.
This marketing & sales strategy optimally takes advantage of social networks to find the right people, with the goal of converting them into long-term customers and achieving the sales goals.
Instead of approaching customers without them having expressed prior interest in the product or service, social selling focuses on sharing content and building lasting relationships. These days, consumers are tired of traditional sales strategies such as phone calls i.e. cold calling and e-mail campaigns.
As a result, attracting the attention of these people is becoming increasingly difficult. Modern consumers are also digitally connected via various platforms, so the modern salesperson has to keep pace.
The transformation for many organizations to social selling
Although sales reps have always been a social activity, social selling has only become a prominent term since the introduction of social media. The amount of information that can be found online about products and services has significantly transformed the sales process.
No longer do consumers have to acquire information from sellers, instead they can do their own research and ask their network for recommendations. It is therefore not surprising that sellers are responding to this trend and establishing themselves on social media platforms such as LinkedIn.
In 2012, IBM introduced a social sales programme, which is now considered to be one of the most successful early examples of social selling.
IBM had a study conducted and concluded that one third of its business partners were already using social media to contact suppliers.
At the time, 75% of respondents indicated they intended to use social media as part of their purchasing process.
Social Selling Index (SSI) and the 4 Pillars of Social Selling
Another forerunner when it comes to social selling is LinkedIn. Several years ago, LinkedIn introduced the Social Selling Index (SSI). Although the concept of SSI isn’t necessarily related to LinkedIn directly, the company lends itself perfectly for examples of proper use of this tool.
Professionals use the tool through LinkedIn to improve their image. At the same time, it serves as a perfect marketing tool for LinkedIn connections.
LinkedIn describes the Social Selling Index (SSI) as the first of its kind. Based on the four pillars of social selling, companies and individuals are rated on a scale from 0 to 100 for their selling abilities. Each pillar has a maximum score of 25.
According to LinkedIn, an increase of this score represents an increase in the seller’s sales success and lead generation. The four pillars are.
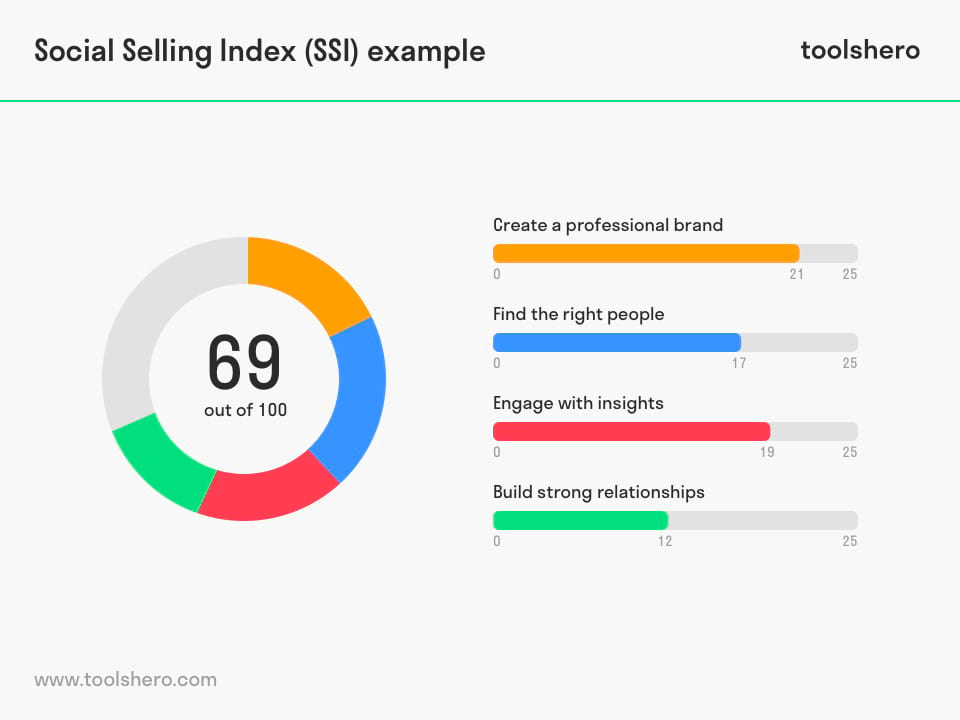
Figure 1 – An example of a Social Selling Index (SSI) overview
1. Create a Professional Brand
When assigning a score in this area, LinkedIn considers the professionalism of the page and personal brand. How complete and professional does the profile look? How many posts are shared? Is there sufficient activity? How many followers does the page have? All these aspects are considered for the score.
It is important that the professionalism of the organisation is immediately apparent from the page itself. It should be clear what the company stands for; including its mission, vision, and expertise in a particular sector.
You can compare it to a personal meeting. For those it is also important to have a ‘professional brand’. Clothing, body language, intonation of voice, and word choice are all important, for example.
2. Find the Right People
Internet and social media make is easier to identify potential customers. To optimally take advantage of the various possibilities, it is necessary to apply account mapping.
Account mapping determines what types of profiles should be contacted and what techniques are most profitable. LinkedIn’s lead builder system shows relevant insights about this.
3. Engage with Insights
LinkedIn defines this pillar as sharing and discovering valuable information in order to create or maintain a relationship with a potential customer. It measures involvements in terms of number of shares, likes, and comments on shared posts.
4. Build Strong Relationships
When it comes to social selling, this fourth pillar is the most important. It combines the first three pillars in a strong and long-term customer relationship. In this relationship, relevant information is shared, honest conversations are conducted, and the customer’s needs are put into focus.
This pillar measures how successful an organisation or individual is when it comes to expanding the network. The larger the network, the greater the chance that there is someone who is interested in learning more about a product.
Social media groups and social selling
By entering the domain of social media, sellers are already in an area with lots of potential. After all, social media groups are ideally suited for finding a certain prospect, providing a great source for new leads. The sales team first determines in which groups the target audience is most active. Examples include: Quora, Facebook groups, LinkedIn groups, etc.
These groups can then be used to collect valuable information about customer demands and pain points. Information and other valuable content can be shared, and assistance can be provided for solving problems or answering questions customers may have about the products or services.
Customers also conduct their own research into the product or service to be purchased. Because sellers are present in the same groups, sellers are part of customers’ research phase.
If valuable information is missing or suggestions are made about the product, the company’s other departments can then start adapting the product to the customer’s demands. This can build trust.
If there’s no group associated with the product or service, this doesn’t necessarily have to be a negative. For example, it could be the perfect opportunity to start a new group and develop a new brand name.
Social selling is also social listening
In addition to the information about sellers who are active in groups on social media, the aspect of social listening is also important.
Social listening is part of effective social selling. Through social media, the reach of companies can be increased in various ways.
Whereas in the past acquiring feedback was complicated, it is now up for grabs.
Social listening is more than just responding to comments and answering questions about the product or service. It is about discovering what is happening in the world of customers, what they’re talking about, and eliminating any problems.
Social listening offers unique opportunities for evaluating customised user experiences and, if necessary, using this information for the optimisation of the company.
Reputation can be monitored and influenced by posting both negative and positive responses.
Now it’s your turn
What do you think? Are you familiar with the explanation of social selling? Are you already using Internet and social media to contact potential customers? To what extent do you believe sellers and marketers can benefit from this marketing & sales strategy? How would you implement a social selling strategy in your own organisation? Which SSI tools do you know? Do you have any tips or additional comments?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Moore, J. N., Raymond, M. A., & Hopkins, C. D. (2015). Social selling: A comparison of social media usage across process stage, markets, and sales job functions. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 23(1), 1-20.
- Belew, S. (2014). The art of social selling. Amacom.
How to cite this article:
Janse, B. (2019). Social Selling. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/marketing/social-selling/
Original publication date: 05/02/2019 | Last update: 04/11/2024
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/marketing/social-selling/”>Toolshero: Social Selling</a>