Behavioral Change Model (Balm)

Behavioral Change Model: This article explains the Behavioral Change Model, developed by Marcel Balm in a practical way. This article contains the definition of the Behavioral Change Model, its stages and practical tips. After reading you will understand the basics of this change management tool. Enjoy reading!
Change behavior
Many people agree that it is difficult to change behavior. Once people are set in certain ways, it will take them a lot of effort to do things differently.
Change behavior has been studied in many instances and has resulted in a variety of theories of behavior, health believe models, social cognitive theory, behavior change techniques, and other methods.
These instruments have helped many people understand their behavior and achieve desired behavior. They have also enabled people to carry out effective intervention on all kinds of topics. Behavioral change models also have been made a part of many health education programmes.
However, people are prepared to change but they do not want to be forced. A change process takes patience, knowledge about behaviour and flexibility from both the person who wants to change and from his environment.
The Balm Behavioral Change Model can help you to understand the process during change.
Behavioral Change Model stages
In his Behavioral Change Model, Marcel Balm describes the process people go through during change.
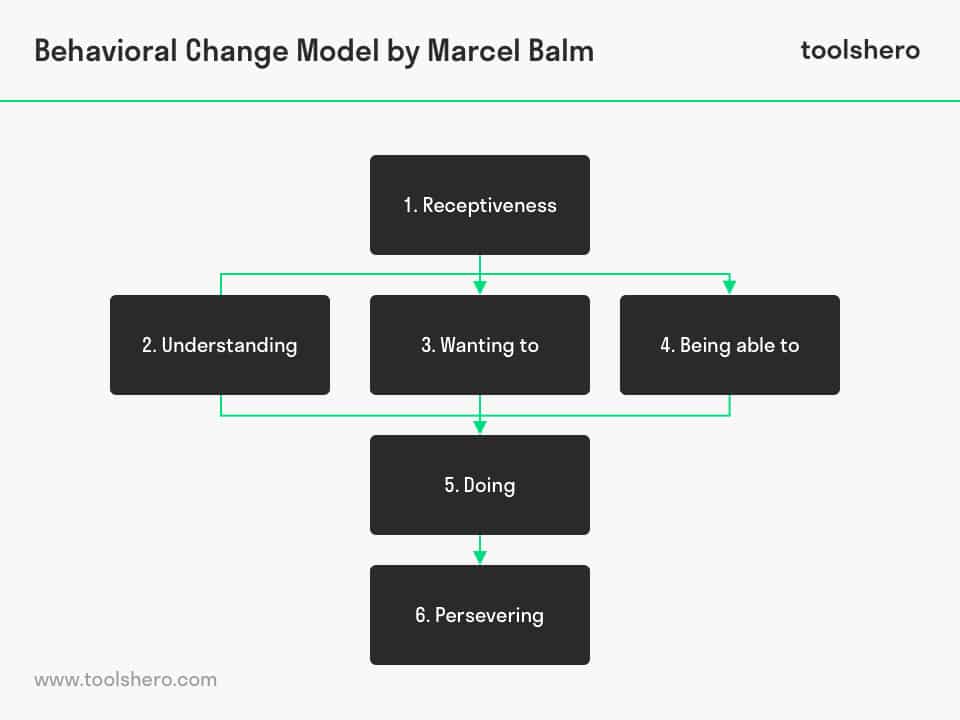
Figure 1 – Behavioral Change Model by Marcel Balm
According to Balm, people go through six stages in the complexity of change:
1. Receptiveness
When someone is not open to change, they are not capable of changing or adjusting their behaviour. Being receptive to new ideas and insights is a first step in the change process.
2. Understanding
According to Balm, people must understand what new behaviour means. When they can describe in their own words what the desired behaviour is and what the advantages are of this new behavior, change is possible.
3. Wanting to
Behavioral change only becomes real when someone really wants to change. The advantages of the new behaviour will outweigh the disadvantages.
4. Being able to
You have to be able to (handle) change. By knowing how new behaviour can be maintained, it will be easier not to revert to old habits.
5. Doing
At this stage of the Behavioral Change Model the change can be put into practice. However, unforeseen difficulties and setbacks will have to be overcome. People should not be distracted by this.
6. Persevering
The newly adapted behavior will must become a second nature and it must be interwoven in the lifestyle. People can only persevere new behavior when they receive positive support from their environment.
Perseverance and the Behavioral Change Model
Behavior can be changed but the question is whether people really want to change. However, wanting to is not the only key to behavioral change. At each stage people will have to become aware of their own responsibility.
Only then will they be able to control the change process. This requires patience as well as perseverance in which a positive result will be an extra stimulus.
Practice
On paper it all seems very logical and easy to bring about change, but in practice the Behavioral Change Model often appears that it is difficult to get rid of certain habits. This has to do with behavior.
Behavior is a meaningful reaction to a meaningful situation. These reactions can be unconscious (automatic) or conscious (controlled).
It is a logical reaction for someone to withdraw their hand when they burn themselves on a hot pan. Unconscious behavior appears to be efficient and adequate but is much more difficult to change than conscious behavior.
Behavioral Change Model and the order of the stages
According to Balm “receptiveness” is a precondition for “understanding”, “wanting to” and “being able to”. These last three concepts arise simultaneously and they in turn are preconditions for “doing” and “persevering”.
Especially the concept of “persevering” will ensure that the new behavior will filter through our system so that it will become automatic, unconscious behavior.
It’s Your Turn
What do you think? Do you recognize the practical explanation of the Behavioral Change Model or do you have more suggestions? Do you see similarities with other theories like the theory of planned behavior? What are your success factors for good organisational behavior change?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Balm, M.F.K. (2002). Exercise Therapy and Behavioural Change. Purdue University Press.
- Hanson, E. M. (1996). Educational administration and organizational behavior. Allyn & Bacon.
How to cite this article:
Mulder, P. (2013). Behavioral Change Model (Balm). Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/change-management/behavioral-change-model/
Original publication date: 03/14/2013 | Last update: 08/16/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/change-management/behavioral-change-model/”>Toolshero: Behavioral Change Model (Balm)</a>












