Denison Organizational Culture Survey (DOCS)

Denison Organizational Culture Survey (DOCS): this article offers a practical explanation of the Denison organisational culture model and Denison Organizational Culture Survey (DOCS). After reading, you’ll understand the basics of this powerful management and corporate culture tool.
What is the Denison Organizational Culture Survey (DOCS)?
The Denison Organizational Culture Survey (DOCS) is a research method based on the Denison organisational culture model. This model is the basis for two diagnostic surveys related to organisations: the organisational culture survey and the leadership 360 development survey.
The model measures four essential characteristics of an organisation. These are the mission, involvement within the organisation, consistency, and adaptability.
Each of these characteristics is divided into three indicators. These management practices give the user the basic data necessary to identify cultural shifts needed to achieve company objectives, evaluate them, and adapt them to the strategy. Based on these twelve components, the user develops surveys to research the corporate culture.
Conducting research into the corporate culture based on the Denison organisational culture model provides an accurate idea of what the organisation should implement to achieve better performance.
Origin
The Denison organisational culture model and the Denison Organizational Culture Survey are the result of over 25 years of research into corporate culture by Daniel Denison, and was completed in 1990.
Daniel Denison was previously a professor at the University of Michigan Business School. Now he is a professor of organisational development at the International Institute of Management and Development in Lausanne, Switzerland.
Corporate cultures
Any strong organisation has behavioural norms that are based on ethical values. These make it possible to create a sense of identity and a positive attitude among employees.
Evaluating the corporate culture is considered essential for any business that’s part of an international chain. That’s because the corporate culture is related to the ability to achieve acculturation between different countries.
Despite more organisations acknowledging that culture has an important and direct impact on business performance (quality, safety, continuity, profitability), it’s often unclear what changes are needed exactly to have significant positive effects. Denison’s organisational culture model and the related Denison culture survey are intended to support the roles of internal and external harmony of the organisational culture.
The Denison Organizational Culture Survey has four essential organisational characteristics
The Denison organisational culture model consists of four components that are subdivided into a total of twelve management principles. Here follows an explanation of these important organisational aspects.
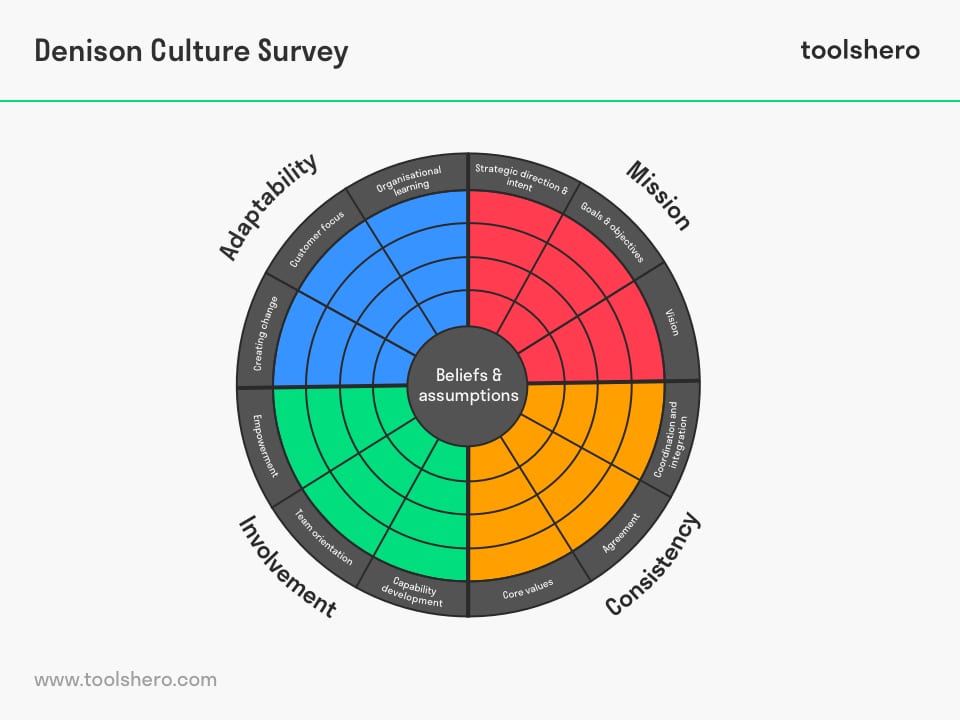
Figure 1 – Daniel Denison organisational culture model
1. Adaptability
An organisational culture’s adaptability tells you something about the extent to which an organisation can observe organisational processes and change them if needed. Adaptability is part of the flexibility quadrant in the Denison model for organisational culture, which also contains the following components.
Creating change
Creating change refers to the welcoming and encouraging of new ideas and the willingness to actually implement change within the organisation. Companies might have a certain aversion against change, but successful businesses actually see change as opportunity. They make it a regular part of the way they do business.
Customer focus
Customer focus refers to the focus on new and existing customers and the willingness to explore new and improved ways and methods to better serve these customers. A successful organisation remains focused on its customers and tries to find ways to meet customer expectations.
Organisational learning
Organisational learning is about acquiring knowledge about the organisation’s successes and failures and taking risks. The core question of this component is: What can we learn to serve our customers in a more focused manner?
2. Mission
The second quadrant in the Denison organisational culture model, and the second topic for the Denison culture survey is the mission.
An organisation’s mission refers to the question why the organisation’s daily activities contribute to shared goals and results. The mission statement is based on stability and is externally oriented.
The following components are related to the mission:
strategic direction & intention
The strategic direction & intention refers to the strategies an organisation uses to determine the right long-term priorities, and that are used to realise the vision.
Goals and objectives
The component goals and objectives is about creating both short-term and long-term goals (SMART). These objectives are created to aid and motivate employees. They help employees gain a better understanding of how their employer’s mission and vision is related to their daily activities.
Vision
The vision is the ultimate reason for an organisation to do business. It shows the organisation’s long-term goal; what it hopes to achieve.
3. Involvement
The third part of the Denison culture survey is involvement. The involvement of an organisation refers to coordinating people within the organisation and creating a sense of ownership, responsibility, and autonomy.
This makes employees feel more like they’re a part of the organisation. This component is based on flexibility and internal focus. Involvement also consists of the following three components:
Empowerment
Empowerment says something about the areas in which employees can make their own decisions, and where they can’t.
Team focus
Team focus says something about the support for employees to achieve individual and shared goals through teamwork. Team focus can either be encouraged, or employees only work for their own results.
Capability development
Capability development is about training, coaching, and developing employees, for instance by trying out new roles and responsibilities. These are important tools for developing new competencies and developing employees.
4. Consistency
Consistency refers to integrating activities, coordination, and monitoring when setting up an internal governance system. Consistency is the final component of the Denison organisational culture model and is rooted in stability and internal focus. Consistency further consists of the following components:
Core values
Core values refer to the set of values that aid consistent decision making.
Agreement
Through dialogue and by looking at a problem from multiple angles, employees and management can achieve agreement on difficult issues.
Coordination and integration
Employees understand how their work impacts the work of others and vice versa. Employees therefore make sure that they coordinate the work to better serve the organisation.
Denison Organizational Culture Survey summary
The Denison Organizational Culture Survey is a research method based on Daniel Denison’s organisational culture model from 1990. The model consists of four quadrants with three components each that represent critical organisational characteristics.
Based on these components, the user creates a survey for employees. The results of these surveys are then analysed by Denison Consulting, who provide the user with a clear report. This gives the organisation better insight into the different departments and the culture and how these can be improved for more effective operation.
Now it’s your turn
What do you think? Do you recognise the explanation of the Denison Organizational Culture Survey? Which aspects of an organisation do you think should also be included in the research into a company’s culture? Do you have any tips or additional comments?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Denison, D. R., Haaland, S., & Goelzer, P. (2004). Corporate culture and organizational effectiveness: Is Asia different from the rest of the world?. Organizational dynamics, 33(1), 98-109.
- Denison, D., Lief, C., & Ward, J. L. (2004). Culture in family-owned enterprises: Recognizing and leveraging unique strengths. Family Business Review, 17(1), 61-70.
- Gillespie, M. A., Denison, D. R., Haaland, S., Smerek, R., & Neale, W. S. (2008). Linking organizational culture and customer satisfaction: Results from two companies in different industries. European Journal of work and organizational psychology, 17(1), 112-132.
- Guidroz, A. M., Luce, K. W., & Denison, D. R. (2010). Integrated change: creating synergy between leader and organizational development. Industrial and Commercial Training, 42(3), 151-155.
How to cite this article:
Janse, B. (2019). Denison Organizational Culture Survey (DOCS). Retrieved [insert date] from toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/management/denison-culture-survey/
Original publication date: 02/10/2019 | Last update: 11/13/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/management/denison-culture-survey/”>toolshero: Denison Organizational Culture Survey (DOCS)</a>












