Strengths Based Leadership (Gallup)

Strengths Based Leadership: this article describes Strengths Based Leadership in a practical way. Highlights of this article include: what strengths based leadership is, what the three keys to effective leadership are and what strengths based leadership involvement, qualities and weak points entail. After reading you will understand the definition and basics of this leadership philosophy. Enjoy reading!
What is Strengths Based Leadership?
Strengths Based Leadership is a book published by the American consultant Tom Rath and the British consultant Barry Conchie in 2013, on behalf of the U.S. Research and consulting firm Gallup Incorporated. The Gallup agency is best known for their opinion polls.
In the book ‘Strengths-Based Leadership,’ leadership styles developed in the past century take the spotlight. Emphasis is placed on the so-called ‘strengths’ of leadership, also referred to as the ‘power of leadership’.
Gallup Strenghts Based Leadership book
In the book, Tom Rath and Barry Conchie reveal the results of 30 years of research that Gallup did to discover the secrets of effective leadership. These ‘strengths’ of leadership have now been embraced by many. The Gallup scientists studied leadership over 30 years. To do so, they studied a million work teams, conducted more than 20,000 in-depth interviews with executives and interviewed more than 10,000 employees worldwide.
Strengths Based Leadership overview
Strength Based Leadership offers a strenghts based approach for leadership. Rath and Conchie identify three keys around the power of management. These three keys form the basis for effective leadership:

Figure 1 – The 3 Keys to Effective Leadership
1. Get to know your own strengths and invest in the strengths of others
By getting the best out of themselves, managers are better able to give this off onto team members. Every person also has their weak points. It’s an art for a supervisor not to emphasise these weaknesses and to try to work around them.
Focusing on strengths helps in leadership. This also applies to the strengths of people in one’s immediate environment. By focusing on what people can do well in an organisation, it leads to big positive changes.
2. When putting together your team, select the people with the proper strengths
Employees like to be selected for their character strenghts. They feel appreciated, which contributes to their commitment and motivation.
When employees are given the opportunity to work on the basis of their own talents and strengths, they will perform better and get more satisfaction from their work. By letting them develop, they will blossom, be more innovative, more helpful and loyal. This ultimately contributes positively to the overall well-being within the organisation.
3. Get insight and subsequently meet the basic needs of your employees
Finding out what employees think is important in their work makes a positive contribution to their work attitude. By responding to this, they will feel more appreciated and will not shy away from doing their best for the organisation. Their loyalty will increase.
Strengths Based Leadership Involvement
In many cases managers believe they are doing a good job, but employees are dissatisfied with their direct supervisor. Gallup’s research shows that employees usually do not find their supervisor people-oriented and empathetic. They find their manager to be a direct and authoritarian person.
They indicate that they desire more room for development, an involved manager and that they want more appreciation for their talents and skills. Strengths Based leadership places the focus on the employee as a person. This is why it’s also referred to as positive or talent-oriented leadership.
According to the Gallup survey, employees who are selected and stimulated on the basis of their strengths are up to 6 times more involved in their job. An effective manager is skilled at tapping into and encouraging the talents and energy of his employees.
It is the manager’s task to ensure that his employees are in the best position and that they can use their talents and strengths to their fullest potential. In addition, managers should fulfil an exemplary role and inspire and stimulate others. This increases their performance, productivity and commitment. These responsibilities also include relationship building. Strenghts Based leaders understand that employees are getting the most out of themselves when the environment allows them to feel comfortable and safe.
Strengths Based Leadership qualities
Strengths Based Leadership is aimed at touching the intrinsic needs of employees and giving them the right support, so that they will rise above themselves. In addition, there are other leadership qualities to achieve effective leadership.
Gallup’s research shows that the perfect leader does not exist. Apart from the fact that specific situations determine one’s style of management, effective managers generally exhibit overlapping characteristics.
They usually have vision and are able to communicate this to their employees. In this way they are passionate and they can stimulate the people around them and involve them in the organisation and its management.
They focus on the process and quality of the execution of the work. The performance can be linked to this. Strengths Based leaders follow progress and in this way support their employees.
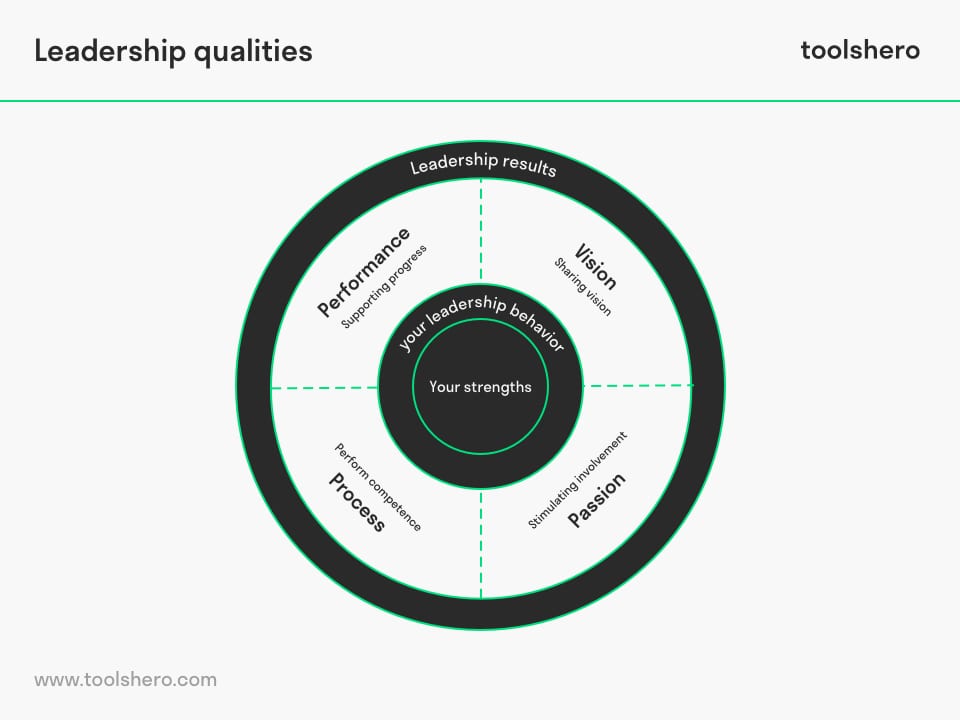
Figure 2 – Gallup Qualities for Leadership
Weak points of Strengths Based leadership
Strengths Based leadership may seem to be one-sided, focusing on the strengths of the managers and their employees. Nevertheless, it is important to also know the weak points of both the manager and their subordinates. After all, weaknesses can pose a performance risk.
Additionally, strengths can be accentuated and can be best used when one is aware of their own weaknesses and knows how to handle them. A transformation occurs when the strengths overshadow the weaknesses and are placed to the right level in the right context. Weak points no longer need to be ignored.
They can receive additional attention and be converted into strengths. It is also possible to compensate for weak points and to ensure that others’ strengths can be appropriately applied. Instead of forcing employees to work on a particular project, it is better to emphasise their qualities.
When every employee knows what they can do for each other on a team, then there’s talk of a ‘best fit’. It is the effective leader who plays an important role in this and motivates and encourages his employees to achieve greater performance.
Now It’s Your Turn
What do you think? What is your experience with Strengths Based Leadership? Do you recognize the practical explanation or do you have more additions? What are your success factors for encouraging and supporting employees in achieving their goals?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Linley, P., Govindji, R., & West, M. (2007). Positive psychology approaches to public services leadership: An introduction to strengths-based leadership. International Journal of Leadership in Public Services, 3(4), 44-55.
- Rath, T., & Conchie, B. (2008). Strengths based leadership: Great leaders, teams, and why people follow. Simon and Schuster.
- Welch, D., Grossaint, K., Reid, K., & Walker, C. (2014). Strengths-based leadership development: Insights from expert coaches. Consulting Psychology Journal: Practice and Research, 66(1), 20.
How to cite this article:
Mulder, P. (2018). Strengths Based Leadership (Gallup). Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/leadership/strengths-based-leadership/
Original publication date: 12/29/2018 | Last update: 08/15/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/leadership/strengths-based-leadership/”>Toolshero: Strengths Based Leadership (Gallup)</a>












