Customer Experience Mapping

Customer Experience Mapping: this article provides a practical explanation of Customer Experience Mapping. After reading, you’ll understand the basics of this powerful marketing tool.
What is Customer Experience Mapping?
Customer Experience Mapping or customer experience journey mapping is similar to customer journey mapping, but they are not the same.
The main difference between the two is that Customer Experience Mapping additionally highlights the emotional element of the customer experience of each brand, product or service instead of solely measuring target customer touchpoints and user experience from pre-sales to after-sales service.
The underlying thought of integrating Customer Experience Mapping is to enhance the corporate understanding of which factors of business customers value. It is additionally used to build long-lasting customer relationships and identifying opportunities.
Customer Experience Mapping is therefore concerned with making continuous improvements in the organization’s product or service offerings so that these products better meet customer’s demands. It is essential here to determine the weaknesses of products (pain points) so that these can be improved and potentially result in customer delight and improved customer retention.
Since Customer Experience Mapping is concerned with the emotion of customers, the tool goes further than customer journey mapping. The similarities of both mapping tools are that both analyze customers’ behavior and company interactions at all customer stages, including awareness, consideration, acquisition, service, and retention, which are examined across all touchpoints and channels.
However, it is essential to note the Customer Experience Mapping is not a linear measurement. It is concerned with attempting to share consistent experiences at all levels of the channels and touchpoints. It is for this reason essential for businesses to view and treat all channels as one instead of treating them as individual channels.
The Customer Experience Mapping process
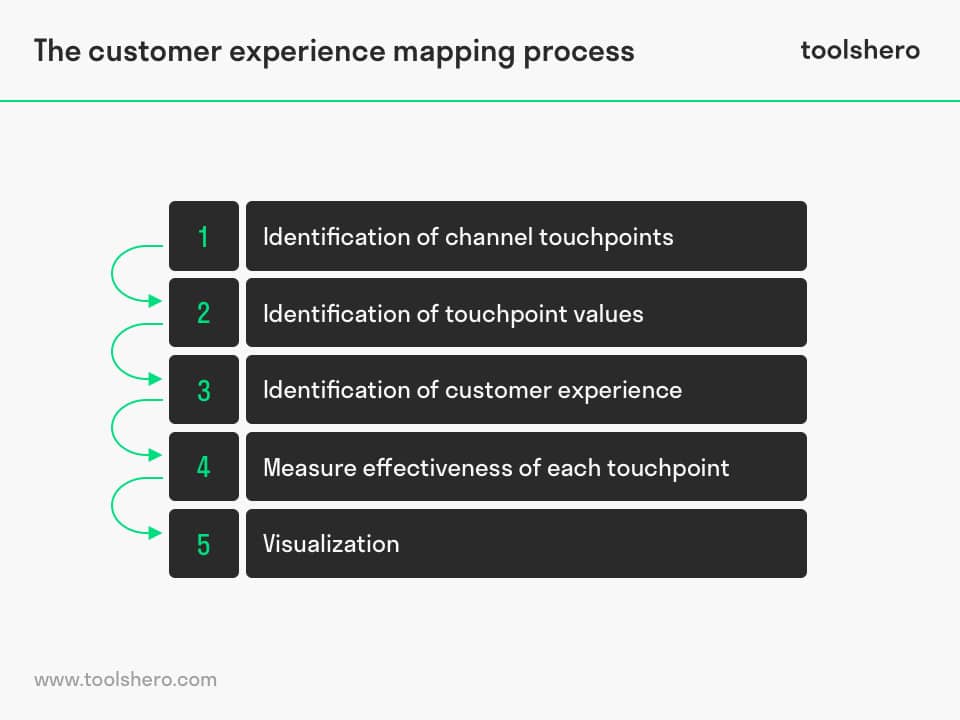
The Customer Experience Mapping process consists of a few necessary steps which should be tailored to each business separately. The few essential steps are as follows and are explained more in detail below: identification of channel touch points, identification of touch points values, identification of target customer experience, measure effectiveness of each touchpoint, visualization.
1. Identification of channel touchpoints
The first step of Customer Experience Mapping is identifying all channels and customer touch points. It means identifying where potential customers are exposed to or use a corporate channel. Touchpoints can for this reason be online and offline.
They are concerned with the points of customer contacts before, during, and after a purchase. Touchpoints could be advertising incentives, social media, websites, catalogs, calls with sales- or customer service representatives, but also outlets and offices.
2. Identification of touchpoint values
In this step of customer experience mapping it is essential from a business perspective to identify what type of experience the firm wants to deliver. It is crucial to identify the reason for existence for each channel, including the underlying goal for the channel.
For example, companies should ask whether a channel should be used solely for creating awareness, proving sales support, or any other purpose. In this way, it becomes easier for the firm to learn what type of user experience should be delivered and how current experiences can further be improved.
3. Identification of customer experience
By this step of Customer Experience Mapping, channel touch points and their related values are identified. It is now essential to map out how customers experience each touch point. The evaluation of this process might differ from one business to another due to the nature of work.
For example, a business that operates in the FMCG industry might evaluate customer touchpoints at the awareness, consideration, acquisition, service, and retention stages. But a company operating in the hospitality industry such as a hotel might evaluate touchpoint at the awareness, consideration, purchase, pre-stay, during the stay, after-stay stages. Companies can for this reason be flexible in how to organize customer experiences.
For effective mapping, data should be gathered. Since Customer Experience Mapping is concerned with the emotional element of consumers, companies need to interact with customers to find channels where customers share their experiences. Obtaining customer insights can be completed by simply conducting surveys or holding interviews. Other ways to gain insights into these experiences is by researching testimonials, forums, and blogs, and other social media channels.
4. Measure effectiveness of each touchpoint
Customer Experience Mapping means continually measuring channel performances. The most basic goal here is to identify the gap between the channel goal and customer experience.
A positive difference means that there is a positive experience, and a negative gap implies that that the channel needs to be further enhanced to a level that causes positive experience. It is crucial to understand what customers experience. It means that companies must do their best to find out customers’ emotions experience during each stage and each touchpoint.
5. Visualization
By this step, it is essential to map out the findings. As explained in step 3, the identification of customer experience, companies can be flexible with deciding how to map out customer stages. The nature of the business is a vital element to evaluate when deciding how to integrate Customer Experience Mapping.
A firm could for example measure channel effectiveness based upon a customer life cycle, which is more a long-term measurement. Another way to measuring a customer brand lifecycle, which excludes the previously mentioned customer stages, but it includes the relationship between aa brand and customer experience.
But businesses can also choose to visualize findings based on customer journeys, which evaluates the effectiveness of each individual channel and touchpoints.
Benefits of Customer Experience Mapping
The integration of creating and maintaining Customer Experience Mapping is associated with improved business performance. Improved performance will become visible in the company’s revenue but also customer feedback. This could substantially result in a healthier company.
Customer Experience Mapping enables a continuous learning process. Not only because a company learns about current customers’ demands, but also because these demands change over time. It is, for this reason, essential to obtain insights about the changing consumer’s preferences.
The result of a better understanding of customers enables a firm to tailor its product offerings more in line with customers’ needs, wants, and demands and stimulate customer engagement. CX mapping is a fundamental approach to improve the perceived value of customers of a company, its brands, and products and service.
As a result of the implementation of customer experience mapping, customer equity will be built over time, which substantially contributes to brand loyalty and customer retention.
Internally, it also brings benefits along. For example, customer understanding and the combination with tailored products are the ideal combinations of knowledge and product offerings to serve customers better. Firms can use the insights of the mapping process to improve the selling process.
Customer Experience Mapping tools
With increased customer expectations of businesses, the demand for specialized tools has increased as well. As a result, developers identified the need in the marketplace for customer experience mapping programs. Consequently, these programs make life easier for business professionals or entrepreneurs to map out customer touchpoints and visualize customer journeys and experiences. Examples of popular tools are listed below.
- Microsoft Visio
- UXPressia
- Realtimeboard
- Heap
- Experience Fellow
Conclusion
Customer Experience Mapping enables a firm to obtain critical insights and pain points that are useful to improve future customer experiences and stimulate customer engagement. While the process seems a long-lasting task due to many customer touchpoints, the benefits of integrating this mapping approach into a work routine are worth it. It enables the company to evaluate every channel, which could result in the visibility of specific points for improvement, but customer experience mapping is also a helpful approach to determine the current positioning in the mind of consumers.
It is essential to note that although it can be important to identify all touchpoints, it can sometimes be more manageable for firms to consolidate a customer experience instead of creating separate customer experience maps for each product. In this way, the evaluation process becomes easier. The bottom line is that there is no single right way to map customer experiences. Every organization needs to find its way of managing data that is most appropriate to the situation.
Now it’s your turn
What do you think? Do you recognize the explanation? What is your view on this tool? Do you have experience with customer experience mapping and would you like to share any additional tips or other comments?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Johnston, R., & Kong, X. (2011). The customer experience: a road‐map for improvement. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal.
- Lemon, K. N., & Verhoef, P. C. (2016). Understanding customer experience throughout the customer journey. Journal of marketing, 80(6), 69-96.
- Millet, G. W., & Millet, B. W. (2002). Creating and delivering totally awesome customer experiences: The art and science of customer experience mapping. Customer Experiences Incorporated.
- Temkin, B. D. (2010). Mapping the customer journey. Forrester Research, 3.
- Tseng, M. M., Qinhai, M., & Su, C. J. (1999). Mapping customers’ service experience for operations improvement. Business Process Management Journal.
- Wolny, J., & Charoensuksai, N. (2014). Mapping customer journeys in multichannel decision-making. Journal of Direct, Data and Digital Marketing Practice, 15(4), 317-326.
How to cite this article:
Zeeman, A. (2020). Customer Experience Mapping. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/marketing/customer-experience-mapping/
Published on: 28/05/2020 | Last update: 26/04/2022
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/marketing/customer-experience-mapping/”>Toolshero: Customer Experience Mapping</a>