Kotler Pricing Strategies

Kotler Pricing Strategies: this article provides a practical explanation of the Kotler Pricing Strategies. After reading, you will understand the concepts of this powerful strategy theory and tool for understanding the internal and external factors that set prices in the marketplace based on the value that consumers place on them. Enjoy reading!
What are the Kotler Pricing Strategies?
The Kotler Pricing Strategies, also called the Nine Quality Pricing Strategies, were developed by the American Philip Kotler, who is considered the father of marketing.
The objective of this theory is to help companies position their products or services in relation to their competitors in the market and to implement the pricing strategy according to the quality that is delivered to the customers.
To find out more about Kotler Pricing Strategies, one must remember and keep in mind what price is and why it is vital in the market.
What is price?
Beyond the financial status and profitability that a business needs in order to be able to balance the economy with the price it offers, it is necessary to understand more than just profits, assets, costs, among other important concepts in order to survive in the market in the long term.
Price is the value of money that a customer or consumer exchanges for a product or service offered by a company. But it is important to identify the added value of the price because apart from having an economic value, it also has a profit value of the product or service delivered.
Price is the value that customers are willing to pay to get what they want, whether out of necessity or luxury. That is why price is a representation of how that product or service is valued in the eyes of the customers.
There are some questions that consumers come to ask when they show interest in acquiring a service / product. Among others questions, they ask themselves do I want to pay a little more for better quality? Do I want to pay less for a lower quality product? What benefits do each of these products offer me?
By identifying the answers to those questions that a potential customer might ask, one can establish basic principles of how customers perceive and evaluate a service or product in their minds before making a purchase. This makes it clear how important the value/ price of that product is that they want to obtain.
The background of the Kotler Pricing Strategies
In order to set a price, the product or service must be based on the three C’s: customers, corporation and competition. These elements interact with the Pricing Strategies Model. According to Kotler there are three strategies to achieve price. These three strategies are taken from Philip Kotler‘s 1967 book “Marketing Management: Analysis, Planning, and Control”.
Pricing based on customer value
This means that the customer is the one who chooses in the end whether to agree to the price or not. The price must show the value that customers have for the product or service.
Competitive pricing
This is when the customer analyses the prices of the competition offering a product or service with the same or similar characteristics at lower or higher prices.
Cost-based pricing: This includes the total costs with production, distribution and sales achieving the perfect balance the company wants according to the costs.
Psychological pricing
The psychological price is to make the client see what he wants to take care of his economy. This is called the level effect, which, by not rounding off a figure, helps the customer visually process the information from left to right and ignore the rightmost digit.
Example $6.99 compared to $7.00 which is positive for numbers ending in 9. It gives the customer the illusion that the product or service they want to have is cheaper since they do not notice the change by the mental game of numbers by lowering the price and not rounding it.
kotler pricing strategies: price as most important factor of the market
Critics opened the debate on the importance of price in the market in which a company wants to be, and how this company can be competitive with the competition with prices and quality offered to consumers.
For Philip Kotler, not all consumers have access to high prices for products or services that companies offer in the market. He believes it is important for organisations to intelligently consider other price versions for those who want to save more in their pocket or who cannot access high prices.
Many people think about the following question: if you buy something cheaper, will the product or service you want to provide be of low or poor quality? How does the company handle an economic balance if prices are lower?
With these basic questions, Kotler generates two options for controlling dams or price pressure:
One is to offer some goods or services at a low price and the other is not to change the price but to add value to that product that will benefit the customer.
According to Philip Kotler there should be three versions of a Good, Better and Best product, these could be called price points as they have several levels of offers and could be more welcomed by the different types of customers that are presented.
Price and Quality Matrix: Nine Quality Pricing Strategies
The Price and Quality Matrix or the Nine Quality Pricing Strategies proposed various levels of the connection between price and quality There are three levels of price: high, medium, low and also three levels of quality: high, medium and low. This relationship gives rise to new pricing strategies resulting in nine items proposed by Kotler which will be understood later in this article.
For the time being we will see in the following graph the relation between price and quality in the matrix:
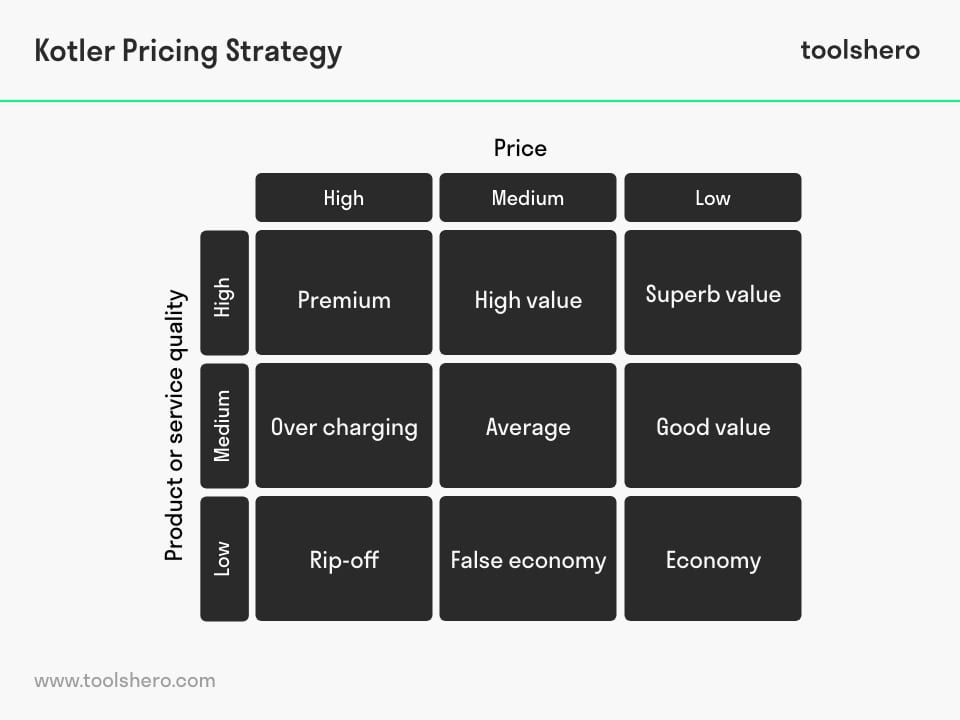
Figure 1 – Kotler nine pricing strategies: price and quality matrix.
The objective of the price and quality matrix is to help position the products / services on the market. It is important for the company to choose the prices so that customers can access what the company offers.
Considering the above, it is also important that the quality of the products / services offered by the organisation complements the price that is put on the market, so that it is consistent with what is planned and what is to be sold.
In this model, Kotler proposes 9 strategies where price and quality interact with each product and service, which are the following
1. Premium – High price / high quality
Premium pricing strategy puts a higher price on the product / service on the market and is of higher quality. This strategy is used when a brand dominates the market.
This means a high price on a product, but an excellent quality that gives popularity in the market as for example the products Apple, Garmin, Rolex among other brands.
2. Overcharging – high price / medium quality
If the quality of a product is good, it can be difficult to raise the price beyond what the product offers.
3. Rip – off price high / low quality
One should stay away from this category because selling a product at a high price but not of good quality will make consumers not believe in the company.
4. High Value – medium price / high quality
To offer a high quality product at an affordable price to customers. This can generate a voice to voice of the product/ service being offered in the market and have good positioning.
5. Average – average price / average quality
This strategy indicates that the value customers pay is similar to the quality of the product or service they are purchasing.
6. False economy – medium price / low quality
Low quality products that are overrated. This is a danger as your customers will alert you to this. It is best to develop a strategy of developing a better product and lowering the price so that it can enter the market.
7. Superb value – low price / high quality
To offer on the market high quality products or services at a low price, accessible to customers.
8. Good value – low price / medium quality
Customers are always looking for a more accessible price on the products and services they want to buy. A strategy to generate more positioning and long life for the company is to give a good value for money that is low and a product quality that is medium.
9. Economy – low price / low quality
It is a strategy that helps to enter a market and achieve future relationships with consumers because it offers economic options, but manages to build a gap between the customers and the company. It is thus an investment in the future.
kotler pricing strategies: how to benefit from the relationship between price and quality?
The relationship between price and quality as set out in Kotler’s Price Strategy can benefit the company within its specific market and empower new customers and link more confidence that will bring long-term positive points.
Also question the timing of your product or service with the above nine items so that you have a more specific and clean picture of where you are in the market and the development and new opportunities that may present themselves according to the type of strategies you want to use to your advantage.
There are some objectives that can be achieved with the strategies:
- Premium strategy for high profit: few competitors, but the brand drives demand with sales at a higher price.
- High value strategy for leadership: higher quality product with more expensive elements.
- Economy strategy for long-term survival: more market share. Updating to what customers want, being ready for changes and being able to adapt easily.
- Low price strategy to grow sales: this is the bet most companies make when they enter a market. They establish low prices in order to be well received by consumers.
Kotler Pricing Strategies summary
Kotler Pricing Strategies are a marketing supplement to establish prices according to the market environment in which you want to be, reviewing the competition. It is important for him that the customer can have several proposals for a product or service from the same company and choose one of them according to his economic capacity.
The company is the one that always has to adapt and shape itself according to what consumers think and want, and with this to be able to implement the appropriate strategies to be well received in the market niches where price is most of the time king.
Also with the price the company can identify and evaluate the market and the product or service they are offering. According to Kotler Pricing Strategies, the company can improve, develop and better organise the services it provides and better satisfy consumers.
It’s your turn
What do you think? Have you implemented Kotler’s Pricing Strategy matrix in your company? Do you see a connection with another pricing model? If so, has this matrix helped you with your product/service? Do you have anything else to add or any suggestions?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Lancioni, R. A. (2005). A strategic approach to industrial product pricing: The pricing plan. Industrial marketing management, 34(2), 177-183.
- Kotler, P. (2012). Kotler on marketing. Simon and Schuster.
- Cravens, D. W., & Piercy, N. (2006). Strategic marketing (Vol. 7). Columbus: McGraw-Hill.
- Kotler, P. (2003). A framework for marketing management. Pearson Education India.
- Kotler, P., & Rath, G. A. (1984). Design: A powerful but neglected strategic tool. The Journal of Business Strategy, 5(2), 16.
How to cite this article:
Ospina Avendano, D. (2020). Kotler Pricing Strategies. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/strategy/kotler-pricing-strategies/
Original publication date: 12/29/2020 | Last update: 11/11/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/strategy/kotler-pricing-strategies/”>Toolshero: Kotler Pricing Strategies</a>






