Birkman Method

Birkman Method: this article describes the Birkman Method, developed by Roger W. Birkman in a practical way. After reading you will understand the basics of this powerful personal and self analysis tool.
What is the Birkman Method?
The Birkman Method is a self-assessment tool, developed by American organisational psychologist dr. Roger W. Birkman about 65 years ago. It allows you to analyse behaviour and profession data with a survey, providing insight into the environment requirements in which people perform best. By means of this psychological personality assessment, different types of people are highlighted.
When Birkman was working as a bomber pilot for the American air force during World War II, he became interested in the question why there were individual differences in the behaviour of pilots.
After the war, he researched the best way to select pilots beforehand. From there, he developed an assessment method and corresponding survey, which provided information about a person’s self-perception and work motivation. The Birkman Method has now grown into a global assessment tool and is a registered trademark.
Birkman Method and self-knowledge
The Birkman Method is about interests, style of behaviour, what motivates people, how they behave in stressful situations and how they can perform more effectively. It also shows the perception and expectations of people. The Birkman Method is also objective and standardised, which makes it a reliable and valid tool.
It’s a self-assessment tool that provides clear insight into the strengths and weaknesses of someone’s working style. It also makes clear what someone’s needs are when it comes to their work environment, where someone’s professional interests lie and which stressful behaviour they show in the workplace. This provides them with more self-knowledge.
In addition to realising one’s own qualities, those of colleagues can also be recognised more easily. In the end, this creates a team that functions better and more effectively. It’s also a tool in creating a personal development plan and/or career guidance. It stimulates pro-activity and taking responsibility.
Online Assessment
The Birkman Method is based on an (online) assessment with over 265 questions. The data of each employee are processed into a report directed at individuals. Using this, a profile is created that consists of sections such as the interests of the person concerned, their own effective style of behaviour, their personal needs, their behaviour in stressful situations. It also offers possibilities for performing more effectively.
According to Birkman, a person’s most optimal style of behaviour can only come out if their personal needs and interests are met. Only then can they blossom. When these needs and interests aren’t met, people can get frustrated and show stressful behaviour.
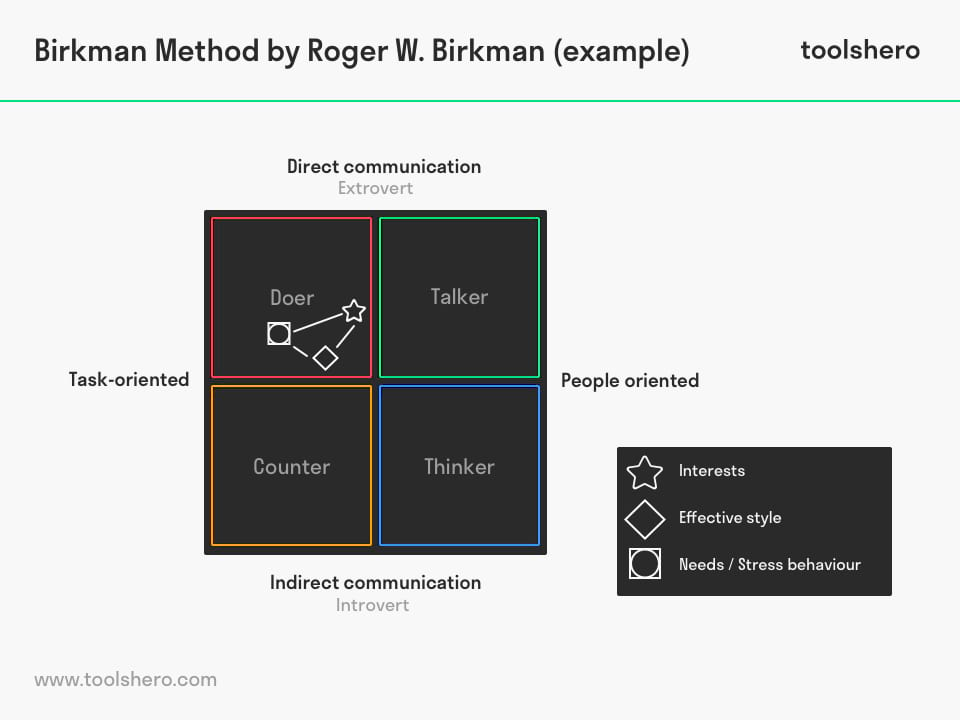
4 Quadrants
In 1921, the well-known Swiss psychiatrist and psychologist Carl Gustav Jung distinguished four basic types of human personality. Jung juxtaposed contrasting functions; thinking and feeling versus perception and intuition. Inner orientation (introvert) and outer orientation (extrovert) play an important role in this.
Apart from Jung, Birkman also distinguishes four main variables, namely direct communication (extroverted) versus indirect communication (introverted) and task-oriented versus people-oriented. In the Birkman model, this combination leads to four personality types, resulting in four visual quadrants that refer to different types of people Each quadrant in the Birkman Method is indicated in their own colour:
- Red quadrant (doer) task-oriented / extrovert
- Green quadrant (communicator) people oriented / extrovert
- Blue quadrant (thinker) people oriented / introvert
- Yellow quadrant (administrator) task oriented / introvert
Birkman Method Symbols
The Birkman Method also uses four symbols, which indicate the preferred action:
Star
This indicates someone’s interests and the type of activities which this person prefers to spend energy on.
Diamond
This indicates the individual’s most effective style. The behaviour someone naturally excels at and which someone shows under normal circumstances.
Circle
This indicates the needs and motivation someone requires. This does not only involve one’s own motivation, but also the support someone requires from others in their environment in order to perform effectively.
Square
This is aimed at people’s stress behaviour and how the normal style of behaviour changes when the individual’s needs are not met.
Behaviours
Each individual has their own interests, qualities, preferred behaviour, needs and stress behaviour. From the different quadrants, specific behaviours can be named:
Blue quadrant
The thinker is characteristically insightful, optimistic, can reflect well and is cautious. The thinker excels at visualising ideas.
Green quadrant
The communicator is characteristically competitive and assertive, they are flexible and respond enthusiastically to new things. The communicator is good in managing and promoting ideas.
Red quadrant
The doer is characteristically friendly and energetic. They are able to think logically, and are clear and decisive. The doer is good in organising and implementing ideas.
Yellow quadrant
The administrator is characteristically a well-organised worker. They are careful, but thorough and ensure ideas are preserved.
Birkman Method: needs and stress
People in the four quadrants respond differently to stress and also have different needs. Below you can find the needs for each quadrant and how they respond in stress situations:
- In the blue quadrant people need personal contact with others. They want to be involved in new activities and prefer discussion with colleagues over executing assignments. They experience stress when there is no social contact, when there are difficulties getting actions going and when this leads to indecisiveness.
- In the green quadrant people need individual confirmation and an active environment. They prefer working autonomously. They experience stress when they are quickly distracted or when they are incapable of properly completing an assignment or when they experience criticism.
- In the red quadrant people need direct and clear authority, an energetic environment, clear work schedules and assignments and business contact with colleagues. They experience stress when they are not clear on what is expected of them and when they need to complete too many tasks in too short a time. They have a tendency to get into a negative spiral.
- In the yellow quadrant people need informal contact with colleagues, complicated and challenging activities and a tight schedule. They like structure and a clear direction and avoid unpredictable situations. This leads to stress. They’re also stressed when there are sudden changes or when they are expected to speak to others about their behaviour. They prefer to avoid this.
Birkman Method and the preferred style
Everyone has a personal preferred style with their own needs, personal interests, organisational focus and stress behaviour. This explains why not everyone would want to work at a large bank, or small advertising agency.
Every individual functions best in their preferred style. For example, doers are energetic and will thrive best in an environment they’re constantly active. Communicators have a competitive mindset and are always eager to try something new.
They’ll prosper in a commercial position. Thinkers are thoughtful and contemplative and prefer to do analytical work. Administrators are mainly conscientious and orderly and appreciate, for instance, financial or administrative work.
It’s Your Turn
What do you think? What is your experience with the Birkman Method? Do you recognize the practical explanation above or do you have additions? What other tips or hints would you like to share?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Fink, S. B., & Capparell, S. (2013). The Birkman method: your personality at work. John Wiley & Sons.
- Larkey, F. R., & Knight, J. L. (2002). Test-retest reliability and the Birkman Method®.
- Birkman, R., Elizondo, F., Lee, L. G., Wadlington, P. L., & Zamzow, M. W. (2008). The Birkman method manual. Birkman International, Incorporated.
How to cite this article:
Mulder, P. (2019). Birkman Method. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/psychology/birkman-method/
Published on: 07/02/2019 | Last update: 04/05/2022
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/psychology/birkman-method/”>Toolshero: Birkman Method</a>