Bronfenbrenner Ecological Model

Bronfenbrenner ecological model: This article explains the Bronfenbrenner ecological model, developed by Urie Bronfenbrenner in a practical way. The article includes the origin of this model, followed by a general explanation per level and the necessary criticism of this model. Enjoy reading!
What is the Bronfenbrenner ecological model?
The Bronfenbrenner ecological model is also known as the ecological systems theory. It serves as a framework for understanding human development, as proposed by Urie Bronfenbrenner, a well-known American psychologist.
The model emphasizes the importance of various environmental and social factors that influence an individual’s development, such as family, school, community, culture and historical context.
The author of the Bronfenbrenner ecological model indicates that human development is a complex and dynamic process shaped by the interaction of multiple layers of influences.
By understanding these influences, the model provides a useful framework in which researchers, educators, social workers and policy makers can better understand and support individuals’ development over time.
Origin of the Bronfenbrenner Ecological Model
The model was developed by Urie Bronfenbrenner, an American psychologist in the 1970s. He was particularly interested in understanding how a person’s environment and social relationships influence their development over time.
Bronfenbrenner was particularly interested in the study of child development and education. He believed that a child’s development is influenced not only by their family, but also by the broader community, culture and historical context in which children grow up.
Bronfenbrenner’s model emphasizes the importance of understanding the various environmental and social factors that influence an individual’s development, as well as the interactions between these factors.
The model consists of several levels:
- The microsystem
- The mesosystem
- The exosystem
- The macrosystem
- The chronosystem
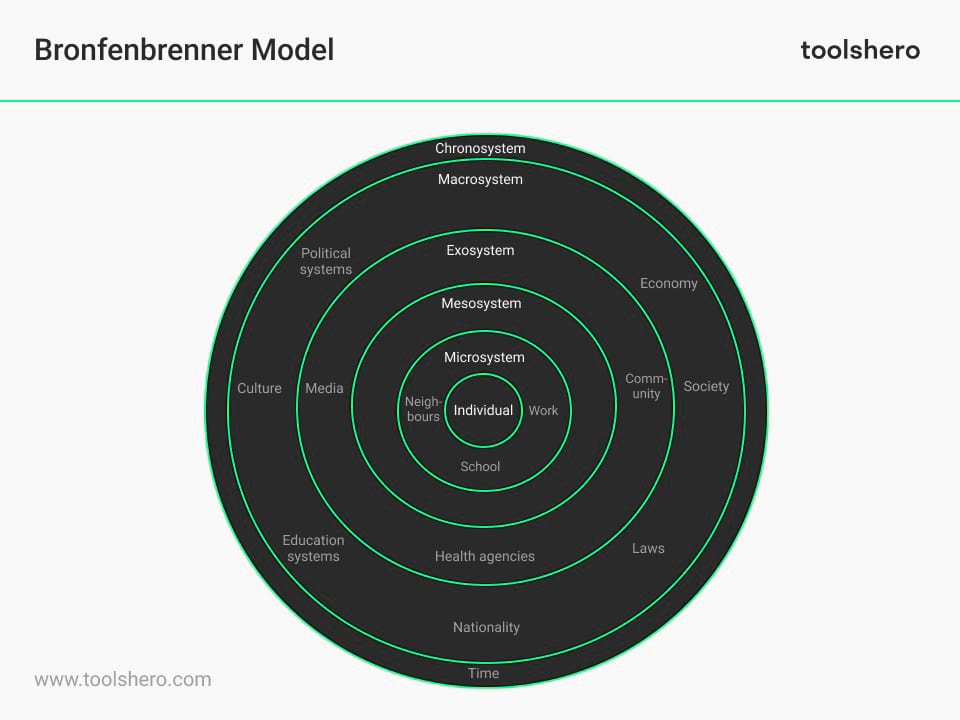
Figure 1 – the levels of the Bronfenbrenner ecological model
All these systems influence the development of a child.
The Bronfenbrenner ecological model is widely used in research, education and social work to better understand how individuals develop and how their development can be supported in a holistic way.
5 Levels of the Bronfenbrenner Ecological Model
The model includes several layers or levels surrounding the person, each with its own unique characteristics and influences. The levels are:
The microsystem
This level includes the people and places closest to the person, such as family, friends, and school. These relationships are most important in shaping the person’s development.
The microsystem is the first level of the Bronfenbrenner ecological model. The microsystem is considered the most influential level of the model because it is where an individual experiences the most social interactions. These interactions can significantly influence their development.
An example. A child’s microsystem can include the parents, siblings, teacher, classmates, and neighbors. The quality of these relationships and interactions, such as the support, warmth, and communication experienced, can shape a child’s emotional, cognitive, and social development.
The microsystem is not isolated and the other levels of the Bronfenbrenner ecological model also affect this level.
The mesosystem
The mesosystem deals with the connections between the different settings in a person’s microsystem, such as the relationship between home and school, between family and peer groups or between parents and teachers. These relationships can support or hinder each other.
An example of this is when a child has a good relationship with a teacher at school and the child’s parents also have a good relationship with this teacher.
The positive interaction between the teacher and the parents can contribute to the child’s development and his or her performance in school. On the other hand, poor interaction between the child’s parents and school can lead to impaired development and reduced performance.
The exosystem
The exosystem is the third level of the Bronfenbrenner ecological model and includes the environments that indirectly influence an individual’s development. This includes, for example, the working environment of parents or carers, the neighborhood or the political and economic environment.
Although the exosystem does not interact directly with the individual, it can indirectly influence development.
For example, if a parent experiences a high level of stress at work, this can affect the way he or she interacts with the child at home and thus indirectly affect the child’s development.
The exosystem shows that the environments that indirectly influence the development of the individual are also important to understand and take into account.
The model therefore emphasizes the importance of the study of all environments that can influence an individual, both directly and indirectly, to gain a more complete picture of the factors that influence the individual’s development.
The macrosystem
The macrosystem is the fourth level of the Bronfenbrenner ecological model. This level encompasses the broader cultural, economic and political context in which the individual finds himself.
It is about the overarching values, norms and ideologies of society, and how these influence the development of the individual.
For example, the macrosystem may relate to national policies in the fields of education, health care, or welfare.
It can also be about cultural traditions, religion and economic factors that influence the development of the individual. The macrosystem influences the other levels of the model and can have indirect effects on the development of the individual.
Understanding the macrosystem is therefore important when developing interventions and policies to support and promote individual development.
The chronosystem
The chronosystem is the fifth level of the Bronfenbrenner ecological model and refers to the role of time in human development. This level deals with how changes in the environment and society over time affect an individual’s development.
The chronosystem encompasses not only the life course of an individual, but also the historical context in which development takes place. For example, changes in technology, politics, economy and culture can influence the development of an individual and his or her environment.
Criticism on the Bronfenbrenner Ecological Model
After its introduction, the Bronfenbrenner ecological model was widely adopted and popular among psychologists and sociologists concerned with child development. This ecological systems theory provides them with a framework for studying the relationship of development and the influence of families in it.
A shortcoming of this model is that not much research has been done on mesosystems, in particular the interactions between neighborhoods and the child’s family. Therefore, it is largely unclear how exactly these systems affect a child’s development.
Another shortcoming of the model is that it is very difficult to empirically test the theory behind the model. Studies focus on establishing an effect, but cannot exclude that it is also these systems themselves that cause the effect.
Assumptions can also be made from the theory, such as that children who do not know a strong ecological system are more likely to lag behind in their development. That may be true in some cases, but many children in difficult situations also develop into complete people and are resilient.
In short, some children who grow up in poverty grow up to be very positive people. The opposite is also true. Some children grow up in a very positive environment, but develop in a negative way.
Now it’s your turn
What do you think? Do you recognize the explanation about the Bronfenbrenner ecological model? Do you agree with Bronfenbrenner’s view that an individual’s development is influenced by their wider community and historical context, as well as family? Can you think of some practical examples where the Bronfenbrenner ecological model could be particularly useful in understanding a person’s development?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Christensen, J. (2016). A critical reflection of Bronfenbrenner s development ecology model. Problems of Education in the 21st Century, 69(1), 22-28.
- Bronfenbrenner, U., & Morris, P. A. (2007). The bioecological model of human development. Handbook of child psychology, 1.
- Bronfenbrenner, U., & Ceci, S. J. (1994). Nature-nuture reconceptualized in developmental perspective: A bioecological model. Psychological review, 101(4), 568.
- Tissington, L. D. (2008). A Bronfenbrenner ecological perspective on the transition to teaching for alternative certification. Journal of instructional psychology, 35(1), 106-111.
How to cite this article:
Janse, B. (2023). Bronfenbrenner Ecological Model. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/psychology/bronfenbrenner-ecological-model/
Original publication date: 10/23/2023 | Last update: 10/23/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/psychology/bronfenbrenner-ecological-model/”>Toolshero: Bronfenbrenner Ecological Model</a>












