Business Model Wheel

Business Model Wheel: this article provides a practical analysis of the Business Model Wheel. After reading, you’ll understand the basics of this powerful strategic tool.
What is the Business Model Wheel?
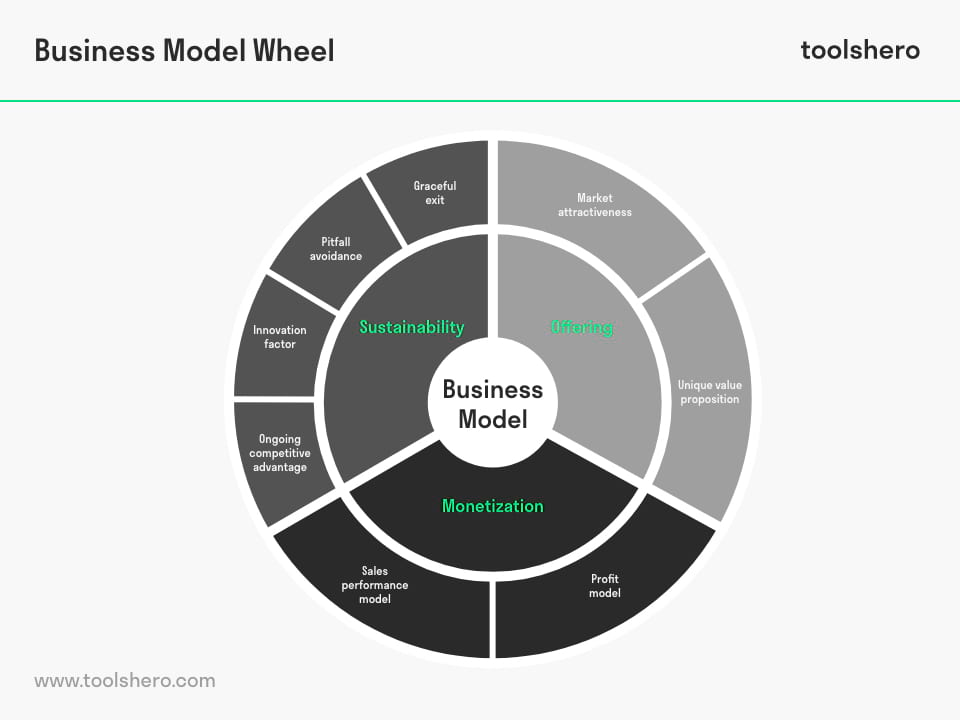
The Business Model Wheel is a practical tool to analyse business models. Business model wheel is a systematic and structured approach for business evaluation, developed by Business Model Institute. The model evaluates business models based on three core elements. These are a company’s offering, monetisation, and sustainability. These three core elements will be further explained in this article.
These three core elements are then subdivided into eight different areas of a business model. The eight areas are:
- Unique Value Proposition (UPV)
- Profit model
- Market attractiveness
- Sales performance model
- Ongoing competitive advantage
- Innovation factor
- Pitfall avoidance
- Graceful exit of the company
By evaluating the eight areas of a business model with the Business Model Wheel, entrepreneurs, managers and others can find the strong and weak points in a business or market.
Additionally, the model can be applied to identify opportunities for innovation. The user of business model wheel can also quantify the eight different areas for assessment in order to set-up and use a Business Model Score.
What is a Business Model?
A business model describes how its value is created, recorded and supplied in an organisation. It essentially clarifies the logic of a company that generates an income. There are many different business models, approaches and methods that are used in the business world, but none of them are suitable for each type of organisation. This depends partly on the organisation, the potential and the desire of the organisation, the possibilities and the internal as well as the external environment of a company.
A good business model articulates the logic of the creation of value. It also provides an image of the architecture of income, expenditure and profit. The question of which elements to determine in designing an organisation depends on the organisation.
To profit from innovation, it is important that corporate pioneers do not only make a difference in product innovation, but also in designing strong business models. It is also important that in designing these, they understand the technological trajectories as well as the ever-changing needs of the client. Developing a profitable business model is not enough to ensure a competitive advantage in the future. This is because it is often easy to imitate a business model.
An example of a widely used method for creating, evaluating or optimising a business model is Business Model Canvas, by Alexander Osterwalder. Business Model Wheel is a variation to this.
Business Model Babson
Babson College is a private business school in Wellesley, United States. This University focuses on entrepreneurship. The symposium for entrepreneurship held at the university attracts many professional entrepreneurs. Among others, the company Rothko Business Growth Management focuses on creating a better understanding of what innovation is, what design thinking in the business world is and what business models are at the core of various companies.
Every organisation has a business model. A shared understanding of what a business model is can be hard to explain. Rothko asked different organisations and received diverse answers, from the description of a product or service or who the target consumer is to competitive profit. None of the answers, however, included an accurate description of the business model.
Core element 1. Offering
The first element of business model wheel to evaluate an existing business model is about what the organisation in question is offering. What does this company offer to its consumers? This core element is subdivided into two parts.
Market attractiveness
This is about the opportunities in the market that the company deals in. Specifically, it is about the branch in general, the niche and the essential client segments in them.
Unique Value Proposition (UVP)
The Unique Value Proposition is the importance to stand out in the market and how the offering of a company can do that.
Core element 2. Monetisation
The second element of the business model wheel method is studying the ways in which a company generates income. How does the company sell products, receive the money and turn this into a profit? This core element is subdivided into two parts.
Sales performance model
The sales performance model is about turning the marketing plans and prognoses into paying customers. Different tools and techniques are available for this. Some are more effective than others, which is why this part is one of the most important areas on which a business model is evaluated.
Profit model
The profit model is about the income arising from the sales techniques and the offering of the organisation. An important part of this is the financial margins in the production and sales of the products.
Core element 3. Sustainability
The third and last element in evaluating business models with business model wheel is the sustainability of a business model. How sustainable is this business model? How does a company ensure that this business model remains effective in the future? This core element is subdivided into several parts.
Ongoing competitive advantage
The ongoing competitive advantage is about keeping the competitive advantage for as long as possible. This is essential in terms of increasing and keeping a large market share and, as a consequence, profit opportunities. Therefore the business model wheel emphasizes development of useful differentiation and advantage in the present and the future.
Innovation factor
The innovation factor is about finding a balance between the need for constant innovation to stay ahead of the competition and the potential of an organisation to do that. It is important that a balance is maintained between these two in order to designate too many nor too few resources to specific activities such as innovation.
Pitfall avoidance
Avoiding pitfalls is important to ensure that a good existing business model does not succumb to setbacks. Pitfalls are things like regulations, overconfidence, lawsuits, fads, trends, and untimely intervention and response to changing market demand.
Graceful exit
The last element of business model wheel is about creating a business model that enables the owner to sell the business for a large sum of money or to stay in the company as CEO emeritus.
The difference between a business model and a business plan
A business plan is a document in which entrepreneurs can lay out the business strategy, as well as the projected financial achievements in years to come.
The business model, as explained in this article, is the mechanism by which entrepreneurs and their companies generate profit. Despite the fact that the business plan plays an important role in the business model, they are two different things.
The business model provides a description of how the specific company is positioned in the market, the segment, and the complete value chain.
Furthermore, it describes the nature and maintenance of relationships with suppliers, clients and partners with the aim of generating as much profit as possible. A business plan translates this vision towards positioning to a series of actions and measures, and then quantifies the impact of these actions in a projection.
Now it is your turn
What do you think? Are you familiar with the explanation of business model wheel? Can you see similarities between this model and models like Business Model Canvas or Business Model You? What other elements of a good business plan do you consider important? Can you use the information in this article to evaluate your own business model and to measure its effectiveness? Do you have any tips or comments?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Voelpel, S. C., Leibold, M., & Tekie, E. B. (2004). The wheel of business model reinvention: how to reshape your business model to leapfrog competitors. Journal of change management, 4(3), 259-276.
- Wirtz, B. W. (2011). Business model management. Design–Instrumente–Erfolgsfaktoren von Geschäftsmodellen, 2.
- Brea‐Solís, H., Casadesus‐Masanell, R., & Grifell‐Tatjé, E. (2015). Business Model Evaluation: Quantifying W almart’s Sources of Advantage. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal, 9(1), 12-33.
- Schweizer, L. (2005). Concept and evolution of business models. Journal of General Management, 31(2), 37-56.
How to cite this article:
Janse, B. (2021). Business Model Wheel. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/strategy/business-model-wheel/
Published on: 01/26/2021 | Last update: 05/12/2022
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/strategy/business-model-wheel/”>Toolshero: Business Model Wheel</a>