ASE model by Hein De Vries explained

ASE model: This article provides a practical explanation of the ASE model. In addition to what the model is, this article also explains the Intent and Behavior, Skills and Barriers, and External Variables. After reading you will understand the basics of this psychology and behavior analysis tool. Enjoy reading!
What is the ASE model?
The ASE model is a model that shows how behavior change takes place. The framework is based on Albert Bandura ‘s Theory of Planned Behavior and Social Learning Theory.
The model states that human behavior can be predicted by studying the intention of behavior. Intention is influenced by Attitude, Social Influence and self Effectiveness (ASE).
The ASE model was developed by Hein de Vries in 1988. Today it is mainly used in the Netherlands and Belgium to help people change their behavior when it comes to health and food intake.
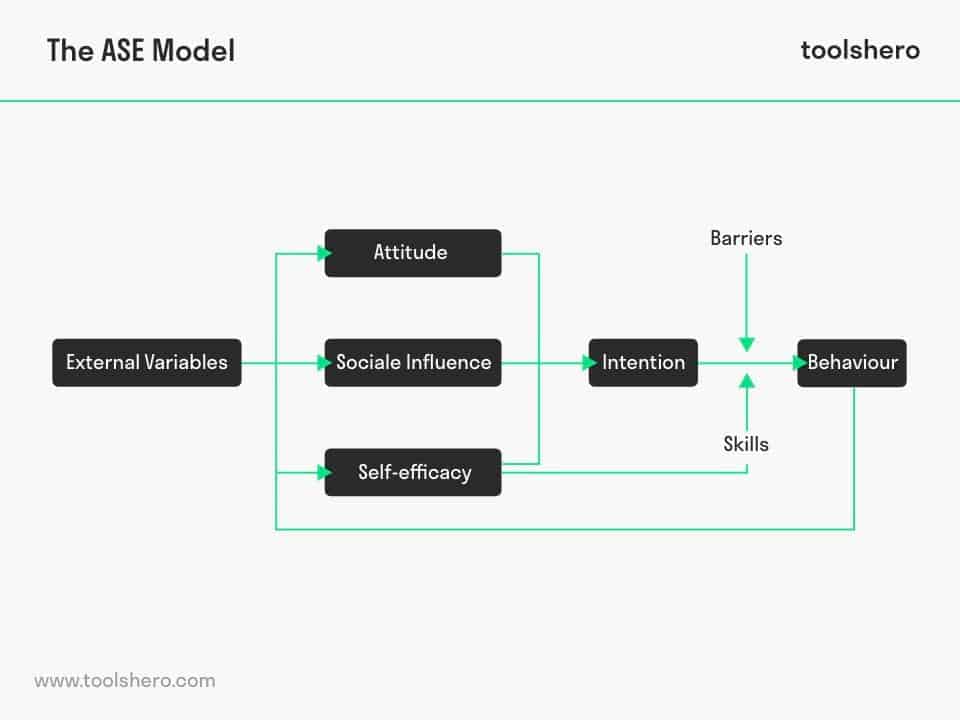
Figure 1 – ASE Model by De Vries
ASE Model: intention and behavior
The intention to instigate behavior means that people intend to behave in a certain way. For example, in the context of this model, people often plan to eat healthy or go to the gym regularly. If there are enough attractive aspects associated with this planned behavior, then people will get the intention to actually display that behavior.
But often enough people have decided to start exercising, but in the end it doesn’t happen. Anything can happen that ultimately makes it impossible. One reason for this is the existence of thresholds, also known as barriers. It also happens that the skills that make it possible to show certain behavior are missing.
ASE model: skills and barriers
An example of a person who would like to do something, but suffers from a barrier, is an older person who cannot move enough per day because of physical obstacles. Another example is that someone is not able to plan well, so that time for sports is often lacking. There are also people who set goals that are not attainable at all.
So having the skills and capabilities is critical. If these are not sufficiently present, the intention may be to do something, but the ultimate behavior will not take place.
The intention for new behavior can quickly disappear. A good example of this are the good intentions people have at the beginning of the year. In the first month of the year it is often remarkably busy in the gym. Soon the interest wanes and a person has fallen back into the old pattern.
Sustainable intention to actually do something, i.e. to display new behaviour, does not just happen. The intention is largely determined by:
- Attitude
- Social Influence
- Self-Efficacy (belief in one’s own abilities)
These terms are explained below.
Attitude
In order to have an intention for a certain behavior, a person must first of all have a positive attitude towards that behaviour. Questions that people ask themselves are: what do I think of sports? How would I like to move more? The starting point is what this new behavior can bring us. For example: I want to set a good example for someone. Or: more exercise is healthy and could mean a longer life.
If certain behavior yields sufficient results and there are no other major objections, then a so-called positive attitude towards new behavior arises. This attitude is fairly stable, but does not yet ensure that behavior will actually be performed. Many people are not negative about more exercise, but they don’t do it.
A positive or negative attitude towards behavior usually stems from past experience. If you have a positive experience with behavior, the attitude is often positive. If you’ve had a negative experience, the attitude is probably negative as well.
In addition, the attitude is also partly based on beliefs. For example, on the belief that exercise is healthy. Or that moving is fun. An attitude can also arise from a habit. Once exercise becomes a habit, that behavior will likely be seen for a long time to come.
Social influence
Our own attitude towards behavior is important, but the opinion of others also counts. This even plays an important role. A person’s social environment influences that person’s behavior in several ways.
Thus, there is a subjective standard. The environment expects people to behave in a certain way and people like to live up to that standard.
Another form of influence is social support. If someone experiences social support, there is a greater chance that certain behavior will be displayed. If the behavior is disapproved, most people will think twice whether they are going to show that behavior.
Social pressure is a third form of influence. Experiencing pressure causes some people to do things they would rather not have done otherwise. There is a good chance that despite some good intentions, behavior will turn out differently in a group.
The influence of the social environment is not only determined by what others really think, but also by what the person thinks the environment thinks. This phenomenon is called normative beliefs. These expectations may be different from what they really are.
Believe in yourself
The third component of the ASE model is self-efficacy. This is also known as believing in your own abilities. This is necessary as well to perform certain behavior. It simply means that one must be able to perform the behavior. It’s not about what people can actually do, but what they think they can do. These are two different things.
Self-efficacy can be related to self-confidence. Some people already think that they won’t last, before they start exercising. If we believe in our own abilities, the chance is greater that certain behavior will be displayed.
ASE Model and external variables
There are other external variables as well that influence whether or not the intention for certain behavior is shown. This includes, for example, age, gender, education level, social status and other personal characteristics. These factors influence behaviour, for example the age of a person can be part of the decision whether or not to participate in sports.
Criticism on the ASE model
The ASE model for behavior change is based on rational thinking and does not take into account other factors that can influence behavior. An example of this is emotional factors. In addition, the model takes little account of unconscious behavior and habits. These can stand in the way of behavioral change. That is a major shortcoming of the model.
For that reason, the model is criticized. The model was therefore later tackled and expanded by the Integrated-change Model, also known as I-change. The I-change model encompasses a broader overview of factors that play a role in behavioral change. The parts of the ASE model are also included.
Conclusion
The ASE model shows that actually displaying the intention of certain behavior is only possible with a positive attitude. In addition, it is important that the social environment is behind the person. Self-efficacy is also indispensable: belief in one’s own abilities.
Now it is your turn
What do you think? Do you recognize the explanation of the ASE model? Can you use this model to better understand your own behavior? What other models for behavioral change do you know? Do you see similarities with other models or theories? What comments or tips can you share?
More information
- Heimlich, J. E., & Ardoin, N. M. (2008). Understanding behavior to understand behavior change: A literature review. Environmental education research, 14(3), 215-237.
- Strecher, V. J., McEvoy DeVellis, B., Becker, M. H., & Rosenstock, I. M. (1986). The role of self-efficacy in achieving health behavior change. Health education quarterly, 13(1), 73-92.
- Marcus, B. H., Selby, V. C., Niaura, R. S., & Rossi, J. S. (1992). Self-efficacy and the stages of exercise behavior change. Research quarterly for exercise and sport, 63(1), 60-66.
How to cite this article:
Janse, B. (2022). ASE model (De Vries). Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/psychology/ase-model-vries/
Original publication date: 08/02/2022 | Last update: 04/17/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/psychology/ase-model-vries/”>Toolshero: ASE model (De Vries)</a>












