EFQM Model explained

EFQM Model: this article explains the EFQM Model in a practical way. This article discusses: what EFQM is, what the quality model is aimed at, what the process looks like, what the five phases in an EFQM assessment are and how the model can be applied. After reading you will understand the basics of this quality model. Have fun reading!
What is the EFQM Model?
EFQM is an acronym that stands for: European Foundation for Quality Management. EFQM was founded in 1988 with the objective to create a platform where organizations can learn from each other to continuously improve their performance for the long term.
Benchmarking with other European organizations will lead to sustainable economic growth.
EFQM wants to create a culture, support managers and directors in training, sharing ideas and innovating with the aid of the so-called EFQM model as a common framework.
The EFQM Model or EFQM business excellence model is the most popular quality management tool in Europe, used by more than 30.000 organisations to improve performance, create sustainable results and driving performance. It supports you to self-assess and reflect. 84% of our members say that the EFQM model helps to improve their organisation.
The EFQM Model
This quality management model and management framework aims at sustainable excellence in which quality, efficiency and sustainability are the key elements. The basis of the EFQM Model consists of the Total Quality Management (TQM) concept.
It consists of a universal framework of concepts, thus enabling organizations to share information in an effective way, irrespective of the different sectors, cultures and life stages in which they are located.
Organizations can thus take other organizations as a model, so that they obtain insight into how far they meet the image of a high-quality organization. The EFQM consists of nine criteria that are subdivided into five Enablers and four Results for managing change and improving performance:
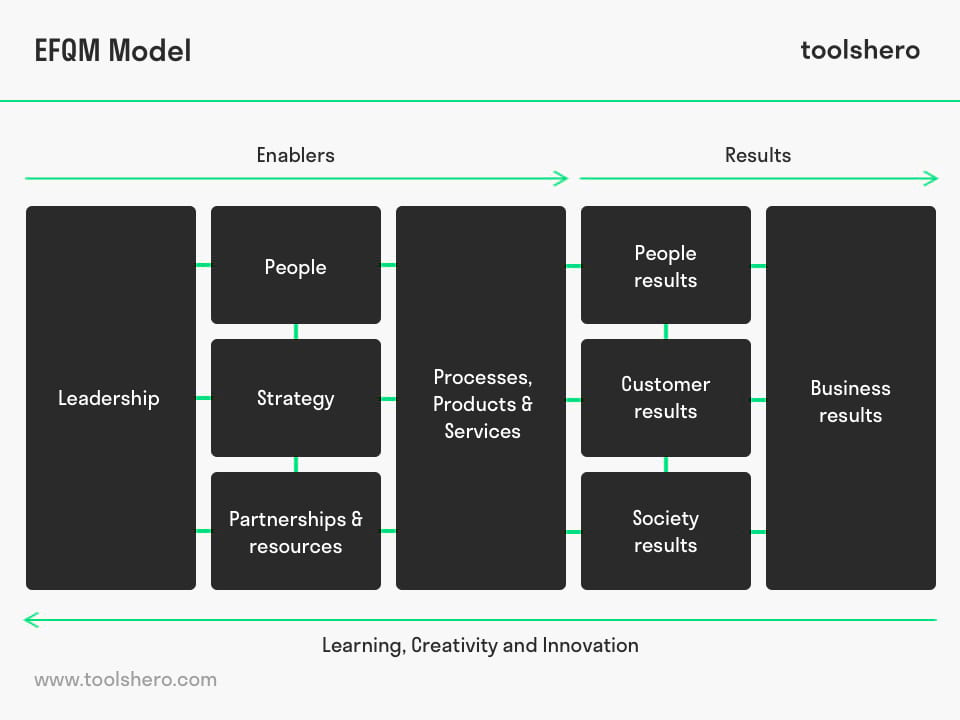
Figure 1 – the EFQM Model / Framework
The five organizational areas indicate how these objectives can be achieved:
- Leadership
- People
- Policy & Strategy
- Partnerships & Resources
- Processes
The four results indicate what the intended objectives are:
- People Result
- Customer Result
- Society Result
- Key Performance Results
Continuous process
The EFQM Model must be read from right to left, as a result of which it becomes clear that the result areas focus on ‘what can be achieved?’, after which it becomes clear that these organizational areas focus on ‘how can these results be achieved?’.
The bottom arrow, ‘learning, creativity and innovation’ indicates that measuring, evaluating and adjusting are not one-off actions but a continuous process. In the same process organizations complete a step by step development.
EFQM Model for Self Assessment
The EFQM Model consists of an EFQM assessment, as an assessment tool that enables an organization to determine where they are in the quality process. The assessment starts with a review of the results. This is the underlying principle of this model.
To improve results, measures should be taken in at least one of the organizational areas. The EFQM Model and the assessment give insight to what level of maturity an organization is in.
This is represented in five development stages:
Stage 1: Activity oriented
The emphasis is on the separate activities within an organization, the activities are determined by working instructions and house rules or by the professionals themselves. Dependencies are given little attention.
Stage 2: Process oriented
The process and control of the process are the key elements, in which powers, duties and responsibilities are clearly defined. Improvements are only made after evaluation has taken place.
Stage 3: System oriented
The organization is looked at as a whole. Control of the processes is about internal and external customer orientation in which cooperation is important. Trends and developments are responded to after they have been identified.
Stage 4: Chain oriented
There is a good control over the entire organizational process including the relationship with suppliers, customers and other partners in the chain. Knowledge, capacity and experience are optimized by periodical self-reflection and are deployed to the best of the organization’s ability.
Stage 5: Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) and Continuous improvement / Gemba Kaizen are anchored in all layers of the organization.
By regularly measuring performance, quality remains high and trends and developments are adjusted preventative.
At this stage the organization can be characterized as a high-quality organization.
Application of the EFQM model
The assessments allow an organization to gain insight as a management system into the quality of its current operational management. Improvements are formulated and these can be implemented by an organization in stages. The assessment itself consists of five steps:
- setting standards for all of the nine key areas
- determining the current quality of operational management
- formulating and prioritizing of improvements
- application and inclusion of improvements in the various (annual) plans
- actual implementation and monitoring of the remedial actions
It’s Your Turn
What do you think? Is the EFQM Model applicable in today’s modern economy and marketing? Which stages do you recognise or are there more? What are in your opinion the success criteria to implement the EFQM Model?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- EFQM, (2013). EFQM Excellence Model. Website EFQM, available at https://www.efqm.org/.
- Martín-Castilla, J. I., & Rodríguez-Ruiz, Ó. (2008). EFQM model: knowledge governance and competitive advantage. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 9(1), 133-156.
- Nabitz, U. W., & Klazinga, N. S. (1999). EFQM approach and the Dutch Quality Award. International Journal of Health Care Quality Assurance, 12(2), 65-71.
- Al-Tabbaa, O. (2011). Boosting Organization Performance Through Adopting Quality Models. Lap Lambert Academic Publishing.
How to cite this article:
Mulder, P. (2012). EFQM Model. Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/quality-management/efqm-model/
Original publication date: 01/20/2012 | Last update: 06/20/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/quality-management/efqm-model/”> Toolshero: EFQM Model</a>













2 responses to “EFQM Model explained”
I see the EFQM Model applicable in today’s modern economy and marketing, the measuring, evaluating and adjusting are continuous process to be follow up, optimized and improved periodically or as per need.
I suggest to have a special tool to set managing by objectives in the organizations / companies.
Thank you for your comment, Sherko.