Total Quality Management (TQM)

Total Quality Management: this article explains Total Quality Management (TQM) in a practical way. It defines TQM, as well as explains its principles. It also offers a practical approach on TQM. After reading this article, you will understand the basics of this powerful quality management tool.
What is Total Quality Management?
Total Quality Management or TQM is an extensive and structured organization management approach that focuses on continuous quality improvement of products and services and long term success by using continuous feedback.
Joseph Juran was one of the founders of total quality management just like William Edwards Deming.
TQM originated in the industrial sector of Japan (1954). Since that time the concept has been developed and can be used for almost all types of organizations such as schools, motorway maintenance, hotel management and churches.
Nowadays, TQM is also used within the e-business sector and it perceives quality management entirely from the point of view of the customer. The objective of TQM is doing things right the first time over and over again. This saves the organization the time that is needed to correct poor work and failed product and service implementations (such as warranty repairs).
TQM can be set up separately for an organization as well as for a set of standards that must be followed- for instance the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in the ISO 9000 series.
TQM uses strategy, data and communication channels to integrate the required quality principles into the organization’s activities and culture.
Principles of Total Quality Management
TQM has a number of basic principles which can be converted to the figure below.
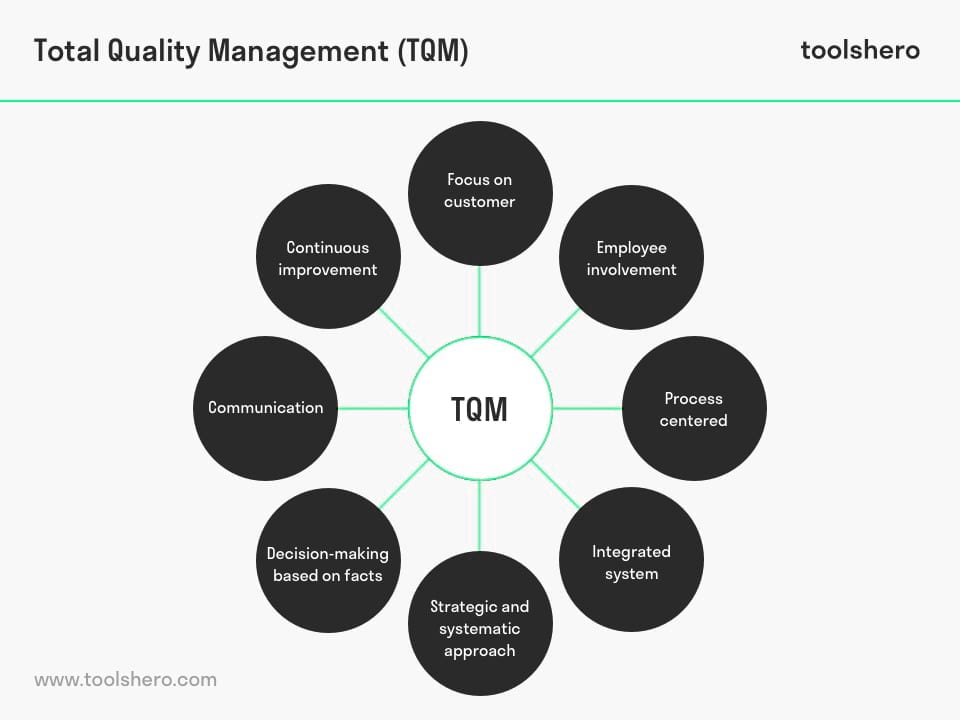
Figure 1 – Total Quality Management (TQM) Principles
Customer focused
When using TQM it is of crucial importance to remember that only customers determine the level of quality.
Whatever efforts are made with respect to training employees or improving processes, only customers determine, for example through evaluation or satisfaction measurement, whether your efforts have contributed to the continuous improvement of product quality and services.
Employee involvement
Employees are an organization’s internal customers. Employee involvement in the development of products or services of an organization largely determines the quality of these products or services.
Ensure that you have created a culture in which employees feel they are involved with the organization and its products and services.
Process centered
Process thinking and process handling are a fundamental part of TQM. Processes are the guiding principle and people support these processes based on basis objectives that are linked to the mission, vision and strategy.
Therefore, focus on process is one of the most important principles of Total Quality Management.
Integrated system
Following the Process centered principle, it is important to have an integrated organization system that can be modelled for example ISO 9000 or a company quality system for the understanding and handling of the quality of the products or services of an organization.
Strategic and systematic approach
A strategic plan must embrace the integration and quality development and the development or services of an organization.
Decision-making based on facts
Decision-making within the organization must only be based on facts and not on opinions (emotions and personal interests). Data should support this decision-making process.
Communication
An effective communications strategy must be formulated in such a way that it is in line with the mission, vision and objectives of the organization.
This strategy comprises the stakeholders, the level within the organization, the communications channels, the measurability of effectiveness, timeliness, etc.
Continuous improvement and Total Quality Management
By using the right measuring tools and innovative and creative thinking, continuous improvement proposals will be initiated and implemented so that the organization can develop into a higher level of quality.
A supporting Total Quality Management tool that could be used is the Deming cycle (Plan-Do-Check-Act) or the DMAIC process.
Total Quality Management (TQM) Certification
Practical approach on Total Quality Management / TQM
When you implement TQM, you implement a concept. It is not a system that can be implemented but a line of reasoning that must be incorporated into the organization and its culture.
Practice has proven that there are a number of basic assumptions that contribute to a successful roll-out of TQM within an organization.
These basic assumptions are:
- Train senior management on TQM principles and ask for their commitment with respect to its roll-out.
- Assess the current culture, customer satisfaction and the quality system.;
- Senior management determines the desired core values and principles and communicates this within the organization.
- Develop a basic TQM plan using the basic starting principles mentioned above.
- Identify and prioritize customer needs and the market and determine the organization’s products and services to meet those needs.
- Determine the critical processes that can make a substantial contribution to the products and services.
- Create teams that can work on process improvement for example quality circles.
- Managers support these teams using planning, resources, and by providing time training.
- Management integrates the desired changes for improvement in daily processes. After the implementation of improved processes, standardization takes place.;
- Evaluate progress continuously and adjust the planning or other issues if necessary.
- Stimulate employee involvement. Awareness and feedback lead to an overall improvement of the entire process. Support this for example by means of a reward model, i.e. Management by Objectives, and recognition.
Now It’s Your Turn
What do you think? Is total quality management (TQM) applicable in today’s modern economy and marketing? What is your experience with TQM? Are the mentioned TQM principles relevant are there new ones?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Dale, B. G., Van Der Wiele, T., & Van Iwaarden, J. (2013). Managing quality. John Wiley & Sons.
- Hackman, J. R., & Wageman, R. (1995). Total quality management: empirical, conceptual, and practical issues. Administrative science quarterly, 309-342.
- Powell, T. C. (1995). Total quality management as competitive advantage: a review and empirical study. Strategic management journal, 16(1), 15-37.
- Blackburn, R., & Rosen, B. (1993). Total quality and human resources management: lessons learned from Baldrige award-winning companies. The Academy of Management Executive, 7(3), 49-66.
How to cite this article:
Van Vliet, V. (2009). Total Quality Management (TQM). Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/quality-management/total-quality-management-tqm/
Original publication date: 03/14/2018 | Last update: 12/21/2023
Add a link to this page on your website:
<a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/quality-management/total-quality-management-tqm/”>Toolshero: Total Quality Management (TQM)</a>













3 responses to “Total Quality Management (TQM)”
Is total quality management applicable in today’s modern economy and marketing? What the answer plz? Thank you
Yea it can be applicable
How total quality management deal with corruption in funding, staffing, etc?